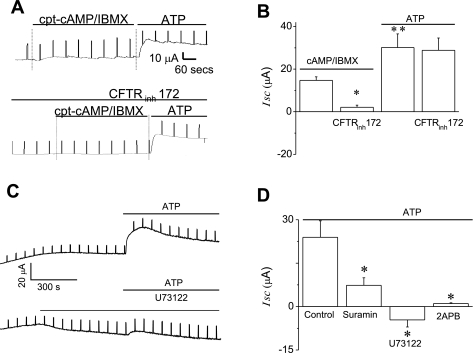
Fig. 9.
ATP increases transepithelial Cl− secretion in polarized biliary monolayers. Short-circuit current (Isc) across normal rat cholangiocyte (NRC) monolayers was measured under voltage-clamp conditions in an Ussing chamber. In these representative recordings agonists are added to the apical chamber. A: simultaneous addition of cpt-cAMP (500 μM) and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX, 100 μM) increased Isc, and subsequent addition of ATP (100 μM) resulted in a further significant increase in the magnitude of the Isc (top tracing). In the presence of CFTRinh-172 (5 μM) cpt-cAMP-IBMX failed to increase Isc; however, the ATP-stimulated increase in Isc was unaffected (bottom tracing). B: cumulative data showing the average change in Isc after addition of cpt-cAMP-IBMX or ATP in the presence or absence of CFTRinh-172. The y-axis values are reported as ΔIsc (maximum Isc − basal Isc). *CFTRinh-172 significantly inhibited the cpt-cAMP-IBMX-induced increase in Isc (P < 0.01, n = 4 each) **Extracellular ATP added to the apical chamber significantly increased Isc vs. cpt-cAMP-IBMX (P < 0.05, n = 4). C: in this representative recording, addition of ATP (100 μM) to the apical bath increases Isc (top tracing). In the presence of U73122, the ATP-stimulated Isc is inhibited. D: cumulative data demonstrating the average change in ATP-stimulated Isc in the presence of suramin, U73122, or 2-APB. The y-axis values are reported as ΔIsc (maximum Isc − basal Isc). *Suramin (n = 4, P < 0.05), U73122 (n = 7, P < 0.01), or 2-APB (n = 6, P < 0.05) each significantly inhibited the ATP-stimulated increase in Isc.