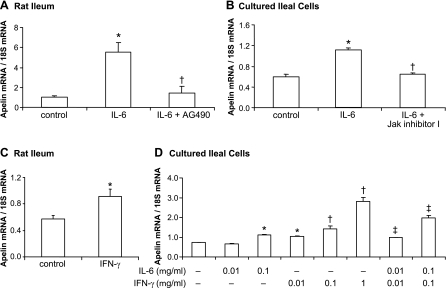
Fig. 2.
IL-6 and IFN-γ-induced apelin expression in vivo and in vitro, blockade by inhibition of a Jak/Stat signaling. A and B: blockade of Jak/Stat signaling reduces IL-6-induced apelin expression in the rat ileum and in primary cultured rat ileal cells. Apelin expression levels increased significantly 24 h after IL-6 treatment compared with control groups. Inhibitors of Jak/Stat signaling (AG490; Jak inhibitor I) were given 1 h before IL-6 treatment (in vivo: 100 ng/rat; in vitro: 100 ng/ml). *P < 0.05 vs. control group; †P < 0.05 vs. IL-6-treated group. C: in rats, ileal apelin mRNA levels increased significantly 24 h after IFN-γ treatment (100 ng/rat). D: in primary cultured rat ileal cells, IFN-γ treatment increased apelin mRNA levels in a dose-dependent fashion (0.01, 0.1, 1 μg/ml). IFN-γ plus IL-6 treatment in combination increased apelin expression levels additively. *P < 0.05 vs. controls; †P < 0.05 vs. control or lower dose; ‡P < 0.05 vs. control or IL-6 or IFN-γ treatment alone. In vivo n = 5 rats/group; in vitro n = 3 dishes/group.