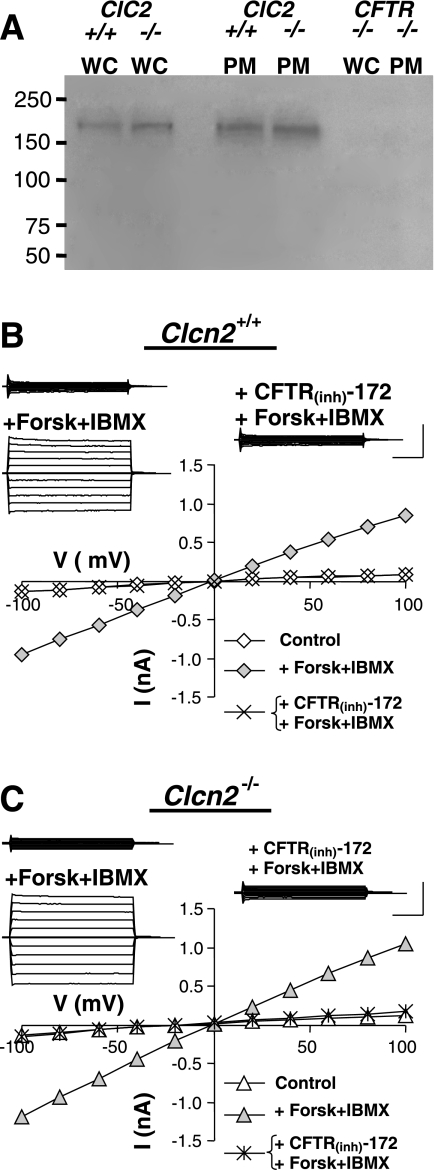
Fig. 5.
Functional expression of Cftr channel protein and cAMP-activated current in submandibular granular duct cells. A: Western blot analysis demonstrating the expression level of Cftr channel protein in the submandibular glands of Clcn2 wild-type (+/+), Clcn2 null (−/−), and Cftr null (−/−) mice. Lanes were loaded with either whole-cell lysate (WC) or plasma membrane fraction (PM). The approximate molecular weight of Cftr is 168 kDa. B: a representative cAMP-activated, Cftr-like current recorded in the presence of 0.3 mM Cd2+ to inhibit the inward-rectifying current. Insets: raw currents recorded in response to 2-s voltage steps from −100 to +100 mV in 20 mV increments from 0 mV holding potential. The currents were recorded before (top left) and after addition of a Cftr activation cocktail (+Forsk+IBMX), and after superfusion with CFTR inhibitor CFTR(Inh)-172 in the continued presence of the Cftr activation cocktail (right). Main panel: current-voltage relation constructed from the raw currents. C: same as in B but the cells were obtained from a Clcn2−/− animal. Calibration bars for current amplitude and time: 0.5 nA and 0.5 s, respectively.