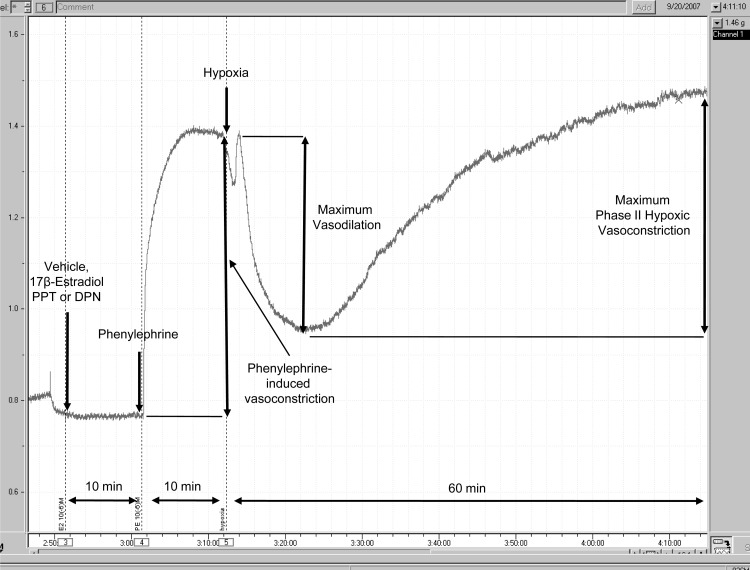
Fig. 1.
Representative pressure tracing of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV) in an isolated pulmonary artery ring. Force in grams is depicted on the y-axis. Time in hours and minutes is represented on the x-axis. Pulmonary arteries precontracted using phenylephrine (PE) (10−6 M) were exposed to hypoxia (Po2 = 35–45 mmHg) for 60 min. Maximum vasorelaxation was measured as the difference between the tension measured when hypoxia was induced (PE-precontraction) and the lowest force preceding phase II HPV. Maximum phase II HPV was measured as the difference between the lowest force preceding contraction and the highest force during 60 min of hypoxia. To investigate for rapid (and, therefore, most likely nongenomic effects), vehicle, 17β-estradiol (E2), propylpyrazole triol (PPT), or diarylpropiolnitrile (DPN) were added to the organ bath 10 min prior to PE and 20 min prior to hypoxia. In the experiments investigating the effect of nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-inhibition on estrogen receptor (ER) signaling during HPV, Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME) was added to the organ bath 30 min prior to the ER agonist.