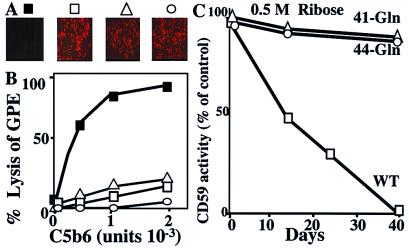
Figure 3.
Site-directed mutagenesis of K41 or H44 abrogates the sensitivity of human CD59 to glycation–inactivation. (A) WT and CD59–Gln-41 or CD59–Gln-44 mutants were expressed in CHO cells. Expression was confirmed by immunocytochemistry by using the anti-human CD59 monoclonal Ab YTH53.1 and fluorescence (Texas red)-labeled anti-rat IgG secondary Ab: ■, transfection vector only; □, WT CD59; ▵, Gln-41 mutant CD59; and ○, Gln-44 mutant CD59. (B) Recombinant WT and mutant CD59 were immunoaffinity purified from CHO cells, and their activity was tested in the GPE hemolytic assay (symbols as in A). (C) Activity of immunoaffinity-purified WT and mutant CD59s before and after glycation with ribose for different time intervals. The points represent the mean of triplicate determinations (SEM smaller than the data points). Representative of three experiments with comparable results.