FIGURE 4.
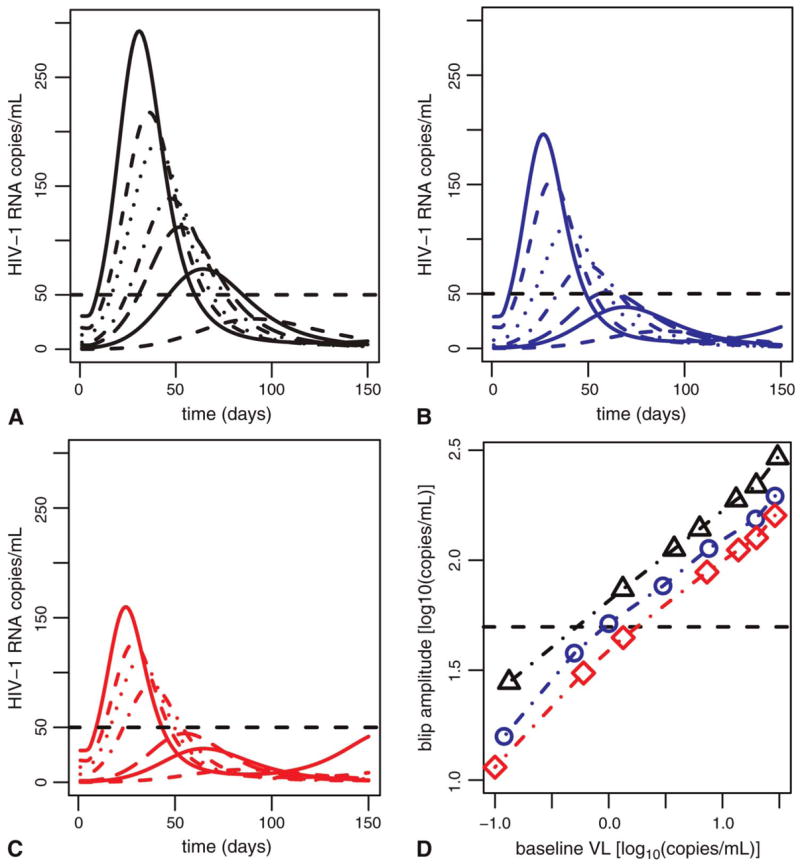
Blip amplitude scales with steady-state viral load (VL) and secondary target pool (drug sanctuary) size. The first 3 panels show results for sanctuaries with a mean size of 1% of target cells in (A), 0.5% in (B), and 0.004% in (C). Different line styles in each frame show blips arising from steady-state viral loads of approximately 30, 20, 10, 7, 3, 1, and 0.1 (HIV-1 RNA copies/mL). To obtain these steady states, we have assumed drug efficacies in the sanctuary population ranging between 0.63 and 0.69 (A), 0.30 and 0.45 (B), and 0.0 and 0.27 in (C) and that λ2 = 99 cells/mL/d (A), λ2 = 57 cells/mL/d (B), and λ2 = 43 cells/mL/d (C). Dashed line shows the assay limit of 50 HIV-1 RNA copies/mL. D, Scaling of peak blip amplitude with target cell pool size and steady-state viral load under treatment. Sanctuary size of 1% (black line), sanctuary size of 0.5% (blue line), and sanctuary size of 0.004% (red line).
