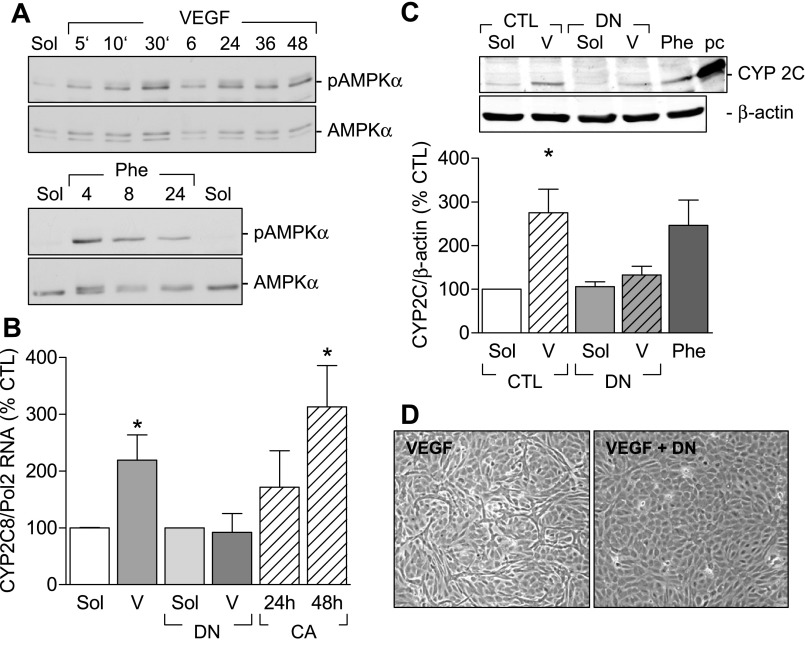
Fig. 5.
Involvement of the AMPK in VEGF-induced CYP2C expression. A: representative Western blots showing the time-dependent (5 min to 48 h) effect of VEGF and phenobarbital (Phe) on AMPK phosphorylation on Thr172. Identical results were obtained in three additional experiments. B: effect of AMPKα mutants on CYP2C RNA expression. Human endothelial cells were infected with either a control virus or a dominant negative AMPKα (DN) adenovirus 48 h before stimulation with either solvent (Sol) or VEGF (V) (30 ng/ml) for 6 h. CYP 2C mRNA was assessed by RT-qPCR. In some experiments endothelial cells were infected with a constitutively active AMPKα mutant (CA), and CYP2C RNA levels were assessed after 24 and 48 h. Effect of the dominant negative AMPKα mutant on the VEGF (V)-induced increase in CYP2C protein expression (C) and tube formation (D) is shown. Phenobarbital (Phe) and a positive control (pc; CYP2C8 overexpression) were used. Bar graphs summarize data obtained in 3–4 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. CTL.