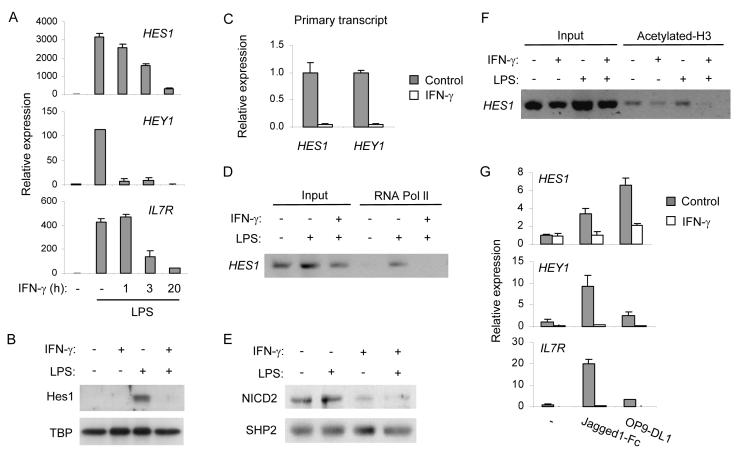
Figure 4.
IFN-γ inhibits Notch responses in macrophages
(A) Human macrophages were primed with 100 U/ml of IFN-γ for the indicated periods and stimulated with 10 ng/ml of LPS for 3 h. mRNA was measured using real time PCR.
(B) Human macrophages were treated with IFN-γ (100 U/ml) overnight, stimulated with 10 ng/ml of LPS, and nuclear Hes1 protein was measured by immunoblotting.
(C) Human macrophages were left untreated or treated with 100 U/ml of IFN-γ overnight. Primary transcripts were measured using real time PCR.
(D) Control or IFN-γ primed human macrophages were stimulated with 10 ng/ml of LPS for 2 h. RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol II) recruitment to Hes1 promoter was assessed by ChIP.
(E) Control or IFN-γ primed human primary macrophages were stimulated with 10 ng/ml of LPS for 6 h. Whole cell extracts were subjected to western blotting using an antibody that recognizes NICD2 (upper panel). The same filter was blotted with anti-SHP2 antibody (lower panel).
(F) Control or IFN-γ primed human macrophages were stimulated with 10 ng/ml of LPS for 2 h. Histone H3 K9K14 acetylation at the HES1 locus was assessed by ChIP.
(G) Human control or IFN-γ-treated macrophages were stimulated with Notch ligands for 3 h. mRNA was measured by real time PCR.
Data in A-G are representative of at least three independent experiments; in A, C and G data are shown as means + SD of triplicate determinants.