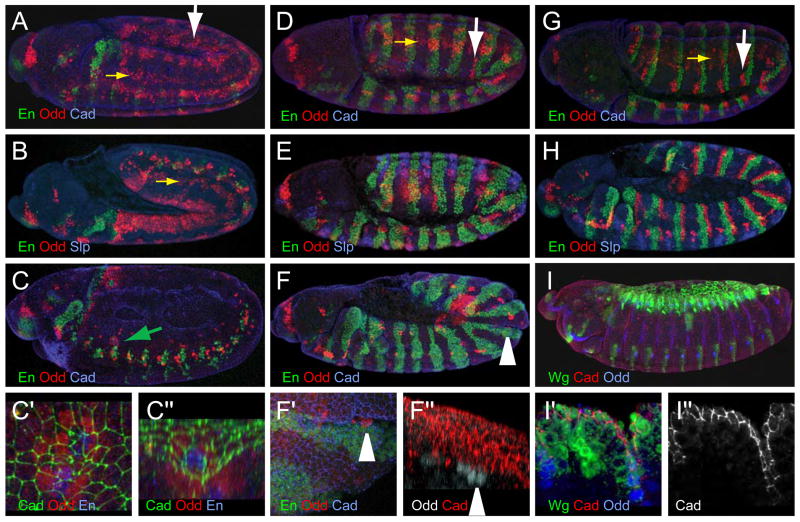
Figure 4. Wg signaling regulates the number of En and Odd cells.
(A–C″) wgIL114 mutant embryos. (A) Stage 10 stained for En (green), Odd (red) and Cadherin (blue). (B) Stage 11 stained for En (green), Odd (red) and Sloppy paired (blue), (C) Stage 15 wg mutant: some En cells (green; green arrow) remain in a thoracic segment, surrounded by Odd cells (red). Cadherin (blue). (C′) Magnification of En cells from (C), with Cadherin (green) showing groove, En, (blue), Odd (red). (C″) 90° rotation of B″. For 3D rotation, see Movie 2 in Supplemental Material.
(D–F″) nkd2 mutant embryos. (D) Stage 10 stained for En (green), Odd (red) and Cadherin (blue). (E) Stage 11 stained for En (green), Odd (red) and Sloppy paired (blue), showing expansion of the En domain and few remaining Odd cells. During retraction, grooves only form where Odd (red) is detected (F; magnified in F′). Cadherin staining (blue) shows that grooves are absent along the En cells (green) not bordered by Odd cells. (F″) 90° rotation of F′ (arrowhead). Odd (gray) and cadherin (red). For 3D rotation, see Movie 3 in Supplemental Material.
(G, H), wild-type embryos. (G) Stage 10 stained for En (green), Odd (red) and Cadherin (blue). (H) Stage 11 stained for En (green), Odd (red) and Sloppy paired (blue)
(I) pannier-Gal4 UAS-wg drives ectopic Wg (green; D′) but does not affect Odd expression (blue; I′) or groove formation (Cadherin, red in I′; I″). Yellow arrows, mesodermal Odd staining; white arrows, ectodermal Odd staining.