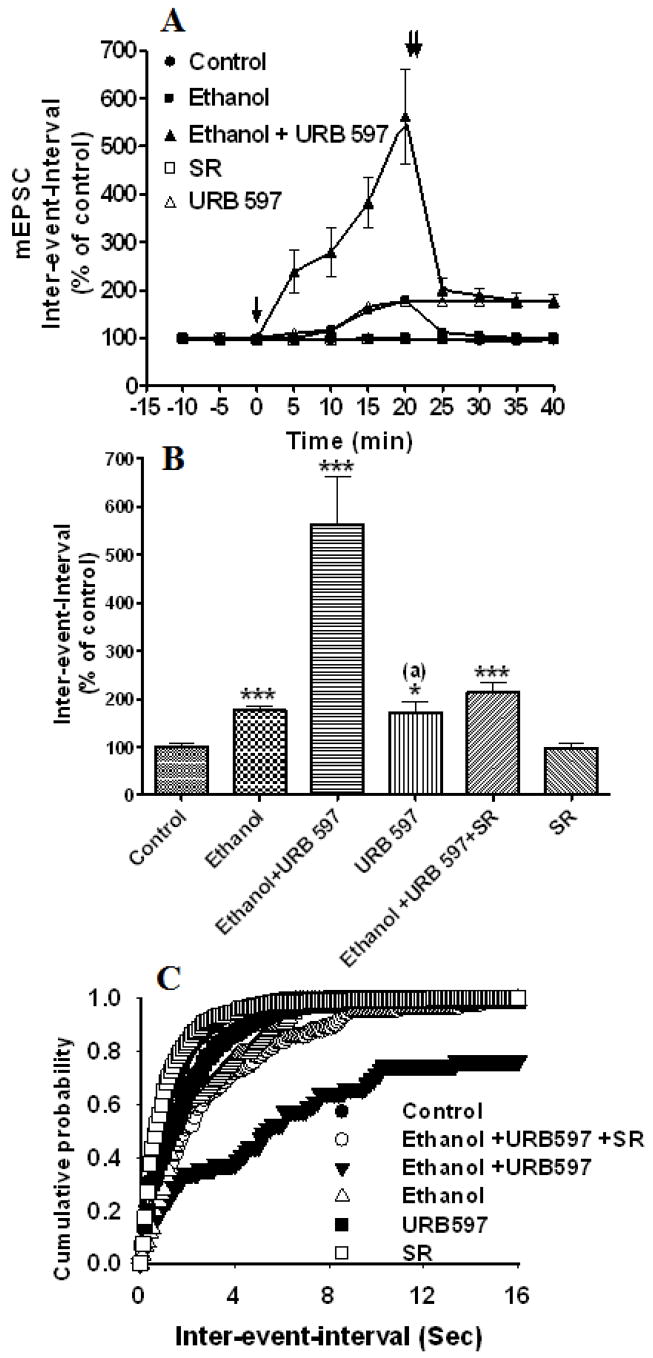
Fig. 6.
FAAH inhibitor, URB597, enhances EC-mediated ethanol-induced suppression of mEPSCs. (A) Application of 50 mM ethanol (bath) decreased the mEPSC frequency (inter-event intervals) (p<0.0001) (n= 4 neurons) of the control. Addition of URB597 to the bath solution in the presence of 50 mM ethanol enhanced the ethanol-induced depression of frequency (inter-event intervals) (n=13 neurons). [↓, Vehicle, ethanol, URB597 or SR141716A (SR) was added to the bath solution; ↓↓, SR141716A was added to the bath solution]. (B) Combined plots of the average inter-event-intervals of mEPSCs under control, ethanol, ethanol + URB597 +SR141716A treatment conditions. URB597 alone significantly depressed mEPSC frequency, probably through the inhibition of endogenous AEA degradation. SR141716A antagonized the effect of URB597 on the ethanol-induced inhibition of mEPSC frequency (n=13 neurons) (***p<0.0001). (a), compared to the control. (C) Average cumulative distributions showing an increase in the mEPSC inter-event interval (sec) in ethanol + URB 597-treated cells relative to controls and ethanol (p < 0.0001; Kolmogorow-Simrnov two-sample test).