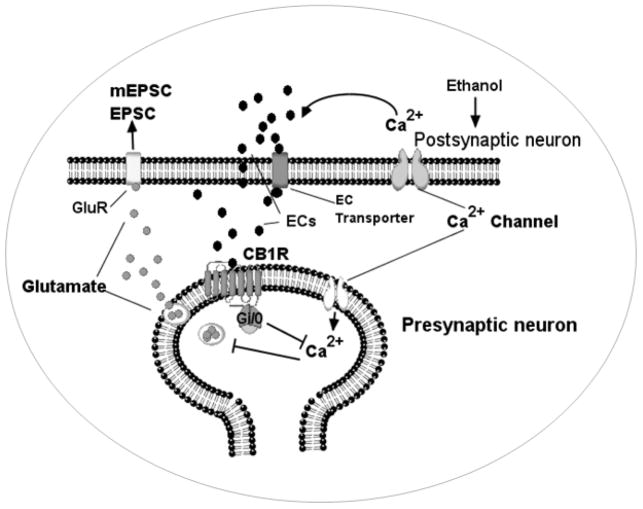
Fig. 9.
A model to show the action of ethanol on excitatory neurotransmission involving ECs and CB1 receptors. The action of ethanol causes the generation of ECs (AEA and 2-AG). These ECs then activate the CB1 receptors (CB1R) at presynaptic terminals and suppress the release of glutamate by inhibiting N-type and P/Q-type calcium channels (Hoffman & Lupica 2000, Huang et al. 2001, Shen & Thayer 1998). GluR, glutamate receptors.