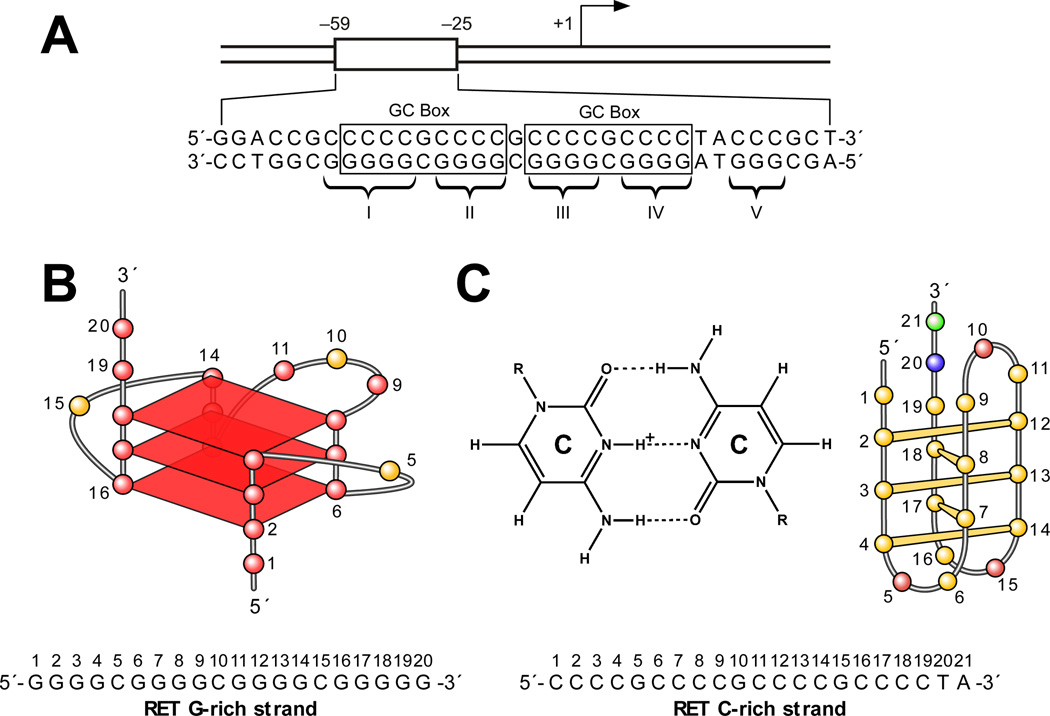
Figure 6.
(A) Promoter structure of the RET gene. Two GC boxes are highlighted. Five guanine tracts (I, II, III, IV, V) are indicated with braces [47]. (B) Proposed G-quadruplex structure for the G-rich DNA oligomer of the RET promoter. The sequence of this G-rich strand DNA is shown under the structure, together with the pol stop sites (arrows). (C) Cytosine+– cytosine base pair in the i-motif (left). Schematic structure of an i-motif formed in the C-rich DNA oligomer of the RET promoter (right). The sequence of this C-rich strand DNA is shown under the structure. (D) Molecular model of the RET promoter sequence (−66 to −19) with i-motif, G-quadruplex, and duplex DNA regions (adenine, green; guanine, red; thymine, blue; cytosine, yellow; potassium ions, white). The symmetrical arrangement of RET C-rich and G-rich sequences is shown below the model.