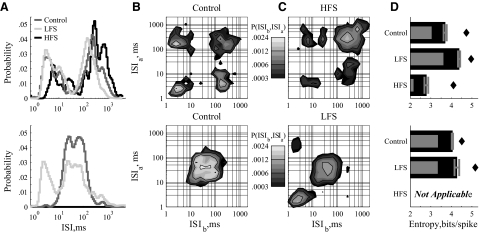
FIG. 4.
Example responses of ventralis anterior (VA)/ventralis lateralis pars oralis (VLo) neurons to LFS and HFS of STN. Two example units (top and bottom) that typify VA/VLo responses. A: ISI distributions show a prominent short-interval burst mode (<10 ms) strengthened by LFS but reduced by HFS. B: without stimulation, some neurons exhibited both irregular spiking and true bursting (top), identified in the joint distributions by a broad slow mode (top right) and a narrow fast mode (bottom left), and the 2 transition modes that connect them (top left, bottom right). Some cells did not exhibit the burst-related modes under control conditions (bottom). C: in bursting cells, HFS greatly reduced the power of the burst and transition modes (top). In nonbursting cells, LFS induced burst and transition modes (bottom). D: LFS increased and HFS decreased firing pattern entropy. Entropy analysis in the HFS condition was not performed on cells that stopped firing in response to HFS (bottom).