FIG. 1.
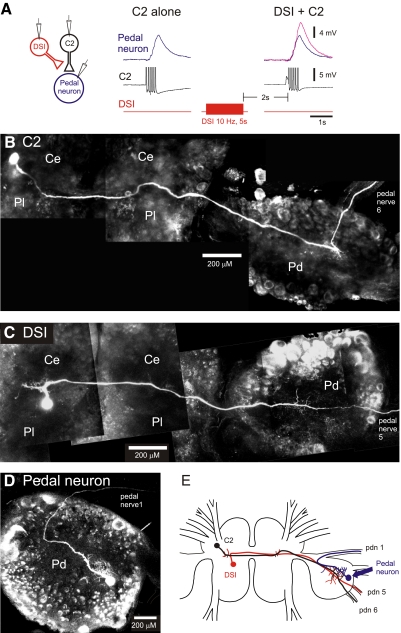
Dorsal swim interneuron (DSI) modulation of cerebral neuron 2 (C2) synaptic strength occurs in the pedal ganglion. A: DSI heterosynaptically increased the size of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) recorded in a pedal neuron in response to C2 action potentials. Intracellular electrodes were placed in C2, DSI, and a contralateral pedal neuron. Action potentials in C2 (5 spikes at 10 Hz) produced a summated monosynaptic EPSP in the pedal neuron. DSI stimulation increased the amplitude of the EPSP (magenta trace). C2 action potentials were truncated in this trace. B–D: composite confocal images of a C2 (B), a DSI (C), and a postsynaptic pedal neuron (D). Neurons were iontophoretically filled with Alexa 594. Both C2 and DSI have somata in the cerebral ganglia and axons that traverse to the contralateral pedal ganglion where they arborize before exiting through pedal nerve 5 (DSI) or pedal nerve 6 (C2). Note that the pedal ganglion was twisted to be ventral side up to facilitate imaging of DSI and C2 neurites. This altered the locations of the pedal nerves in the images. D: a typical pedal neuron that received excitatory synaptic input from C2. Its primary neurite arborized in the pedal ganglion before exiting via pedal nerve 1. E: a composite schematic of the morphology of these 3 neurons (DSI, C2, pedal neuron) showing the site of overlap of their axons in the pedal ganglion. Ce, cerebral ganglion; Pd, pedal ganglion; Pl, pleural ganglion.