FIG. 6.
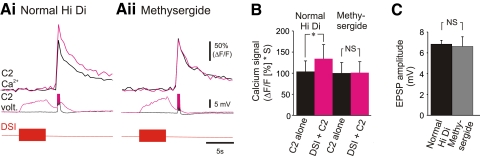
Methysergide blocked DSI enhancement of C2 spike-evoked Ca2+ signals. A: a DSI spike train (10 Hz, 5 s) enhanced C2 spike-evoked Ca2+ signals in the distal neurites (Ai; black trace, C2 alone; magenta trace, C2 stimulation 2 s following the DSI spike train). C2 was stimulated to fire 5 spikes at 10 Hz. Corresponding C2 and DSI voltage traces are shown below the C2 Ca2+ signals; spikes were truncated to highlight the depolarization of C2 caused by the DSI spike train. In the presence of the serotonin receptor antagonist methysergide (50 μM), DSI stimulation no longer enhanced C2 spike-evoked Ca2+ signals (Aii; black trace, C2 stimulation alone; magenta trace, C2 stimulation following the DSI spike train). However, methysergide did not block the DSI-evoked depolarization. B: averaged data showing that in normal Hi Di saline the C2 spike-evoked Ca2+ signals were significantly larger following the DSI spike train; however, in methysergide, there was no significant difference between the Ca2+ signals evoked by C2 stimulation alone or following the DSI spike train {2-way repeated-measures ANOVA (performed using the raw data, with one factor being whether or not DSI was stimulated, and the other factor being Hi Di versus methysergide in Hi Di) with post hoc pair-wise comparisons [Student-Newman-Keuls, F = 8.075 (DSI stimulation. × methysergide), DF between subjects = 4, n = 5]}. Methysergide did not significantly affect the amplitude of the Ca2+ signals evoked by C2 stimulation alone. C: methysergide did not significantly affect the amplitude of the DSI-evoked depolarization of C2 [P = 0.82, paired t-test (mean amplitude in normal Hi Di = 6.84 ± 0.37 mV, mean amplitude in methysergide = 6.62 ± 0.92 mV), n = 5].