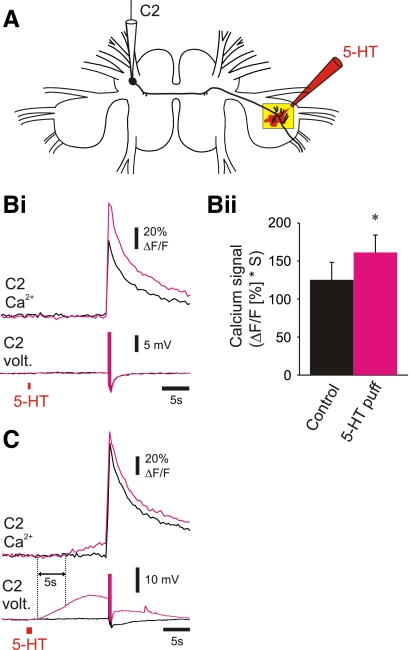
FIG. 7.
Pressure ejection of serotonin mimicked the neuromodulatory effects of DSI but also had additional actions. A: experimental setup: imaging from the distal neurites of C2 with an electrode in the soma of C2 and a puff electrode filled with 10−3 M serotonin positioned just above the ventral surface of the pedal ganglion (illustration of a serotonin puff shown in red). Bi: a puff of serotonin (10 psi, 500 ms, red bar below the C2 voltage traces) given 15 s before the C2 spikes (5 spikes at 10 Hz) mimicked the modulatory effects of DSI on C2 spike-evoked Ca2+ signaling (Bi; black trace, C2 alone; magenta trace, C2 stimulation following the serotonin puff; corresponding C2 voltage traces are shown below the C2 Ca2+ signals; C2's spikes were truncated to highlight the depolarization caused by the serotonin). Bii: averaged data for serotonin puffs given 15 s prior to the C2 spikes in which the serotonin puff did not change resting Ca2+ levels in C2. In these preparations, serotonin significantly enhanced the C2 spike-evoked Ca2+ signals [P < 0.05, paired t-test (mean before serotonin puff = 125.27 ± 23.02, mean after serotonin puff = 161.25 ± 22.96), n = 4], thereby mimicking the actions of synaptically released serotonin. C: in a different preparation from Bi, doubling the pressure and duration of the serotonin puff (20 psi, 1 s) caused a depolarization in the C2 membrane potential recorded in this soma and an increase in basal Ca2+ in C2's distal neurites and increased the size of spike-evoked Ca2+ signals (black trace, C2 alone; magenta trace, C2 stimulation following the serotonin puff; corresponding C2 voltage traces are shown below the C2 Ca2+ signals; C2's spikes were truncated to highlight the depolarization of C2 caused by the serotonin puff). Note that the depolarization of C2 caused by the serotonin puff preceded the increase in C2 basal Ca2+ by ∼5 s (dashed lines at the onset of the C2 membrane potential depolarization and at the onset of the increase in C2 basal Ca2+).