FIGURE 3.
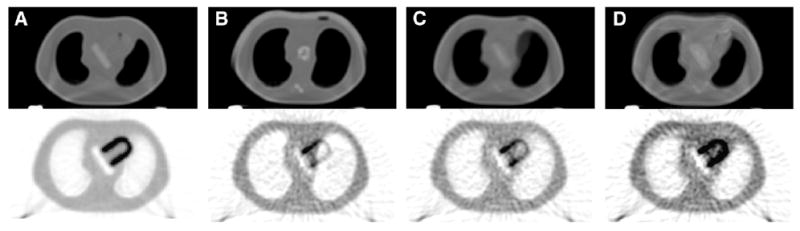
Comparison of attenuation correction techniques for cardiac PET, with CT images for attenuation correction at top and attenuation-corrected PET images at bottom. (A) PET/CT data acquired from stationary phantom processed to induce motion and generate the true case. (B–D) PET data acquired from moving phantom corrected with helical CT, as performed in current clinical practice (B); with average cine CT (C); and with intensity-maximum cine CT (D). The proposed cine methods reduce bias and variance in myocardium.
