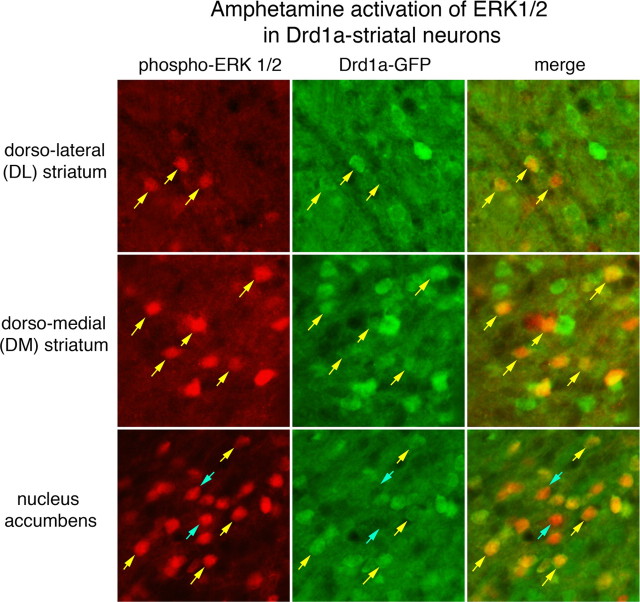
Figure 2.
d-Amphetamine activation of ERK1/2 in Drd1a-expressing striatal neurons. Drd1a-BAC-EGFP transgenic mice were treated with d-amphetamine (10 mg/kg), and brain sections containing the striatum were processed for colocalization of phospho-ERK1/2-IR (red fluorochrome) and GFP-IR (green fluorochrome). A 100 μm2 area of the dorsolateral (DL), dorsomedial (DM), and nucleus accumbens is shown. The numbers of phospho-ERK1/2-immunoreactive neurons vary from few in the DL to many in the nucleus accumbens. In each region, nearly all phospho-ERK1/2-immunoreactive neurons colocalize with GFP (yellow arrows), which is produced in Drd1a striatal neurons. There are some rare phospho-ERK1/2-immunoreactive neurons that are GFP-IR negative (blue arrows) clearly evident as dark lacunas in the background of GFP fluorescence. These data indicate nearly all striatal neurons in which ERK1/2 is activated after d-amphetamine treatment express the Drd1a receptor.