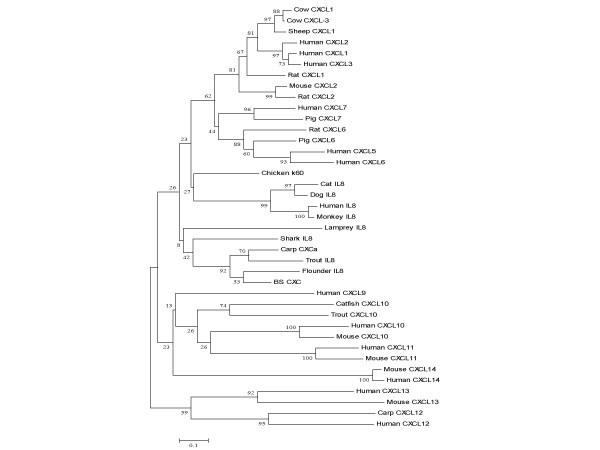
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis. The sequences were aligned by the CLUSTAL W program and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by neighbor-joining methods using MEGA version 2.1. The phylogenetic tree shows the relationship among the full-length amino acid sequences of the BS CXC mature peptide with other representative CXC sequences, Numbers at branch nodes represent the confidence level of 1000 bootstrap replications. The used sequences are represented as follows: human CXCL1 AAP36752; human CXCL3 NP_002081; human CXCL4_p02776; human CXCL5 NP_002985; human CXCL6 NP_002984; human CXCL7 NP_002695; human IL-8 NP_000575; human CXCL11 O14625; human CXCL12_P48061; human CXCL13_O43927; human CXCL14 O95715; chicken K60_CAA75212; Triakis scyllium IL-8 BAB79448; trout IL-8 CAC33585; lamprey IL-8 CAA13114; flounder IL-8 AAL05442; carp CXCa CAD13189; BS CXC AAY18807; cow CXCL1 NP_783631; cow CXCL3 NP_776724; sheep CXCL1 AAB93930; mouse CXCl 2 NP_033166; rat CXCL1 NP_110472; Rat CXCL2 NP_446099; pig CXCL7 AAB28904; carp CXCL12 CAD59916; catfish CXCL10 AAQ01585; trout CXCL10 CAD01141; rat CXCL3 BAA02009; rat CXCL6 NP_071550; dog IL-8 JN0841; monkey IL-8 AAA86705; mouse CXCL10 P17515; mouse CXCL11 Q9JHH5; mouse CXCL13 O55038; mouse CXCL14 Q9WUQ6).