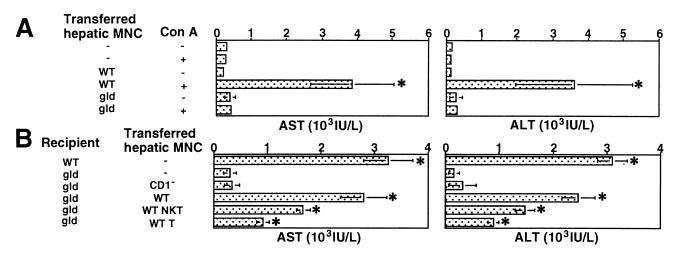
Figure 3.
Critical contribution of FasL on NKT cells for Con A-induced hepatitis. (A) Adoptive transfer of hepatic MNC isolated from wild-type (WT) mice sensitizes gld mice to Con A-induced hepatitis. Total hepatic MNCs (5 × 106 cells) isolated from the indicated mice and/or 15 mg/kg Con A were injected into the liver of gld mice. Sera from individual mice were obtained 6 h after injection, and AST and ALT levels were measured. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of 10 mice in each group. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. *, P < 0.01 compared with Con A-injected gld mice. (B) Adoptive transfer of hepatic MNC from CD1-deficient (CD1−) mice does not sensitize gld mice to Con A-induced hepatitis. Total hepatic MNCs (5 × 106 cells) isolated from the indicated mice or the indicated hepatic MNC subpopulation (2 × 106 cells) isolated from wild-type (WT) mice were injected into the liver of gld mice along with 15 mg/kg Con A. Sera from individual mice were obtained 6 h later, and AST and ALT levels were measured. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of 10 mice in each group. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. *, P < 0.01 compared with Con A-injected gld mice.