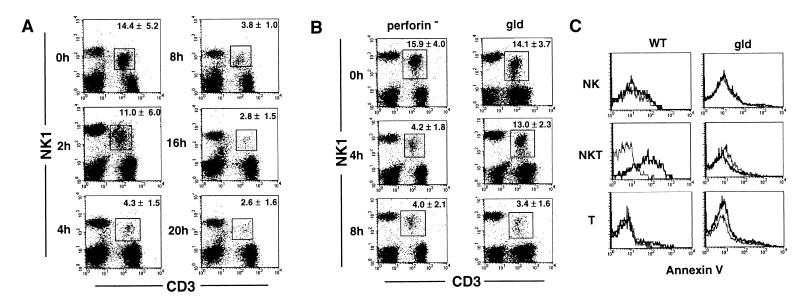
Figure 6.
Apoptotic elimination of hepatic NKT cells after Con A injection. (A) Selective depletion of hepatic NKT cells upon administration of Con A. Wild-type B6 mice were i.v. injected with 15 mg/kg Con A. After the indicated period, hepatic MNCs were isolated and stained with FITC-conjugated anti-CD3 mAb and PE-conjugated anti-NK1.1 mAb. The percentage of NKT cells (boxed) indicated in each panel represents mean ± SD of five mice at each time point. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (B) Delayed depletion of hepatic NKT cells in gld mice. Perforin-deficient mice and gld mice were i.v. injected with 15 mg/kg of Con A. After the indicated period, hepatic MNCs were isolated and stained with FITC-conjugated anti-CD3 mAb and PE-conjugated anti-NK1.1 mAb. The percentage of NKT cells (boxed) indicated in each panel represents the mean ± SD of five mice at each time point. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. (C) FasL-mediated apoptosis of hepatic NKT cells. Wild-type (WT) and gld mice were i.v. injected with 15 mg/kg Con A or PBS only. Hepatic MNC were isolated 2 h later and stained with PE-conjugated anti-NK1.1 mAb and Cy-chrome-conjugated anti-CD3 mAb. Then, annexin V binding assay was performed by using annexin V-FITC apoptosis detection kit. Annexin V binding was analyzed on electronically gated NK1.1+CD3− (NK), NK1.1+CD3+ (NKT), or NK1.1−CD3+ (T) cells. Bold lines indicate the annexin V binding to Con A-injected hepatic MNCs, and thin lines indicate the annexin V binding to PBS-injected hepatic MNCs. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments.