Fig. 2.
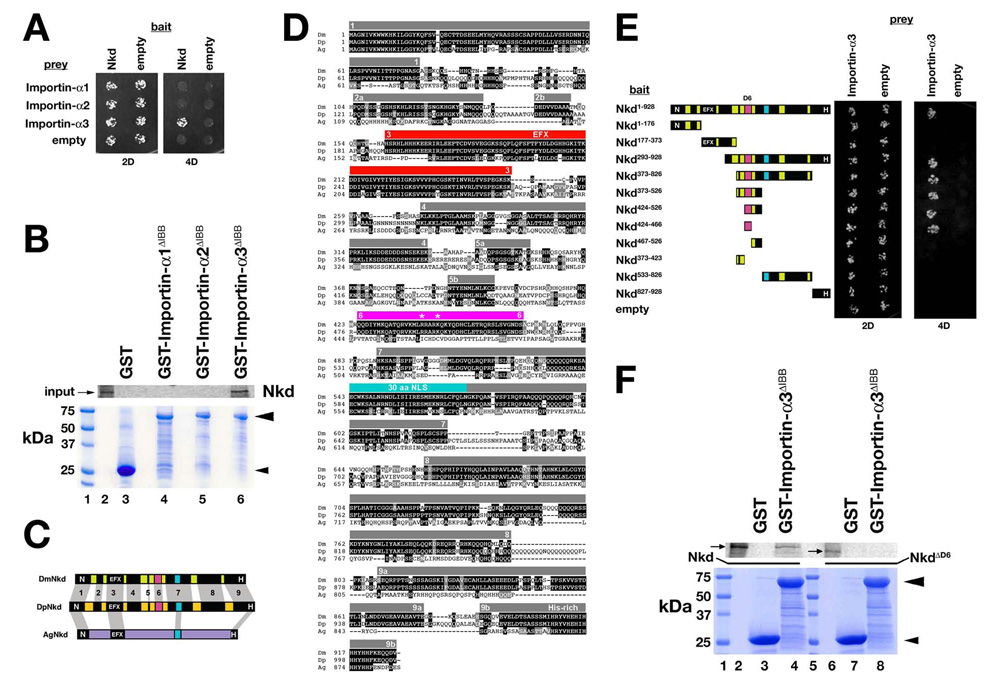
Drosophila Nkd binds Importin-α3. (A) Y2H of strains expressing indicated bait (left) and prey (top) constructs under double (2D) or quadruple (4D) dropout conditions. Only strains with Nkd+Importin-α3 plasmids grew under 4D. (B) GST-pulldown assay showing that in vitro translated Nkd was retained on Glutathione agarose bound to GST-Importin-α3ΔIBB (Importin-α3 residues 118–543 lacking the N-terminal Importin-β-binding (IBB) domain; see Materials and methods) in lane 6 but not to GST (lane 3), GST-Importin-α1ΔIBB (lane 4) or GST-Importin-α2ΔIBB (lane 5). Coomassie stained gel below confirmed that each recombinant protein (arrowheads) was bound to glutathione agarose. Size markers are in lane 1, and 35S-Methionine labeled Nkd input is in lane 2. (C) Schematic of D. melanogaster Nkd (DmNkd), D. pseudoobscura Nkd (DpNkd), and A. gambiae Nkd (AgNkd). Grey bars show sequence similarity. DmNkd/DpNkd have nine regions of similarity, numbered 1–9. Region #6 (D6; magenta) binds Importin-α3. (D) ClustalW alignment of insect Nkd proteins. Amino acid identities are dark-shaded, similarities light-shaded. Grey bars indicate regions of Dm/Dp sequence similarity (numbered). EFX–red; 30aa NLS-light blue; D6-magenta. Asterisks designate basic residues mutated in this work. (E) NkdD6 (residues #424–466) binds Importin-α3 by Y2H. Yeast expressing indicated Nkd deletion constructs were assayed for growth as in panel A. (F) GST-pulldown assay showing that in vitro translated Nkd (lanes 2–4), but not NkdΔD6 (lanes 6–8), bound to glutathione agarose to which GST-Importin-α3ΔIBB but not GST was bound. Coomassie-stained gel shows that equal amounts of each GST fusion protein were bound to the glutathione agarose. Size markers are in lanes 1 and 5, and Nkd or NkdΔD6 inputs are in lanes 2 and 6, respectively.
