Table 4.
Generation of binaphtholate catalysts in situ and conversions (ee) for asymmetric ring closing metathesis (equation 5).
| time (h), temp (°C) | % amide conv (% catalyst) | % substrate conv (% ee) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2[R-Benz2Bitet] |
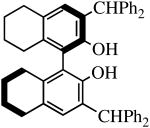
|
R″ = Ar | 8.0, 50 | 100(81) | 77(94)a |
| R″ = Ar′ | 1.0, 70 | 100(100) | 99(97) | ||
| H2[R-TRIP2BINO] |
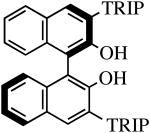
|
R″ = Ar | 48.0, 60 | 100(100) | 82(95) |
| R″ = Ar′ | 48.0, 60 | 100(100) | 99(96) | ||
| H2[R-Ph2BINO] |
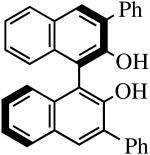
|
R″ = Ar | 0.5, 50 | 100(100) | 90(68)b |
| R″ = Ar′ | 1.0, 70 | 100(100) | 95(87) | ||
| H2[rac-Mes2BINO] |
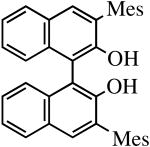
|
R″ = Ar | 14.0, 70 | 100(100) | 75c |
| R″ = Ar′ | 14.0, 70 | 91(86) | 93 | ||
| H2[R-TMS2BINO] |
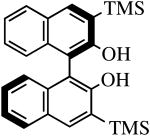
|
R″ = Ar | 8.0, 50 | 82(56) | 92(72) |
| R″ = Ar′ | 36.0, 70 | 90(90) | 99(56) |
