Fig. 2.
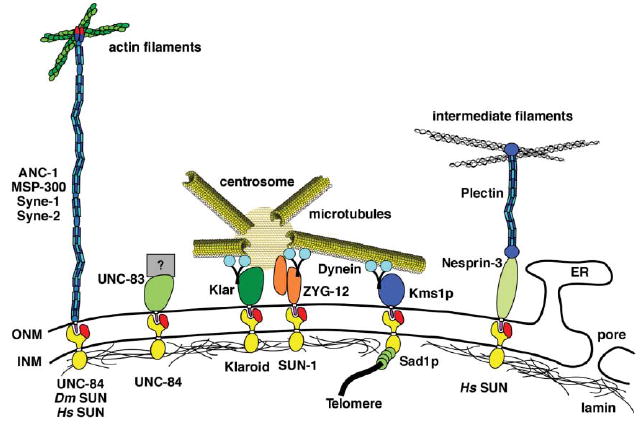
KASH and SUN proteins bridge the nuclear envelope and connect the cytoskeleton to the nucleus. Proteins with SUN domains (red) localize to the inner nuclear membrane (INM) and proteins with KASH domains (purple) localize to the outer nuclear membrane (ONM). Various KASH/SUN interactions from different organisms are depicted here. From left to right: the ANC-1/MSP-300/Syne family connects actin to the ONM, C. elegans UNC-83 and UNC-84 function during nuclear migration by unknown mechanisms, Drosophila Klar mediates dynein and is necessary to link the centrosome to the ONM, unrelated C. elegans ZYG-12 dimerizes to connect the centrosome to the ONM, S. pombe Sad1p and Kms1p transfer the forces from cytoplasmic dynein to move telomeres at the INM, and human Nesprin-3 connects intermediate filaments to the ONM. For more details, see text.
