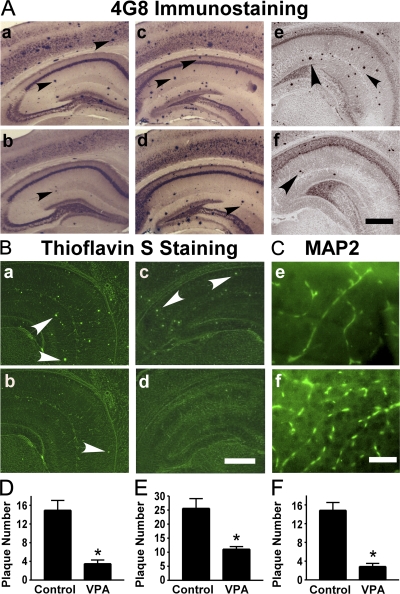
Figure 1.
VPA treatment significantly reduces neuritic plaque formation in AD transgenic mice. (A) APP23 mice at the age of 7 or 9 mo and APP23/PS45 double-transgenic mice at the age of 6 wk were treated with 30 mg/kg VPA for 4 wk, whereas age-matched control APP23 mice received the vehicle solution. The mice were killed after behavioral tests and the brains were dissected, fixed, and sectioned. Neuritic plaques were detected using an Aβ-specific monoclonal antibody 4G8 and the DAB method. The plaques were visualized by microscopy with 40X magnification. The number of neuritic plaques was significantly reduced in VPA-treated mice compared with controls. b, d, and f show the representative brain section of the 7-mo APP23 age group, 9-mo APP23 age group, and APP23/PS45 mice treated with VPA, and a, c, and e show their controls, respectively. Black arrows point to plaques. (B) Neuritic plaques were further confirmed using thioflavin S fluorescent staining and visualized by microscopy at 40X magnification. There were less neuritic plaques in VPA-treated mice (b and d) compared with age-matched control mice (a and c). a and b show brain sections of APP23 mice, and c and d show the brain sections of APP23/PS45 mice. White arrows point to green fluorescent neuritic plaques. (C) The brain sections of APP23 were also stained with MAP-2 antibody. VPA treatment significantly increased the number of MAP-2–positive neurites. Bars: (A and B) 400 μm; (C) 200 μm. (D) Quantification of neuritic plaques in APP23 mice with treatment starting at the age of 7 mo, the number represents mean ± SEM. n = 30 mice each. *, P < 0.0001 by Student's t test. (E) Quantification of neuritic plaques in APP23 mice with treatment starting at the age of 9 mo, the number represents mean ± SEM. n = 12 mice each. *, P < 0.005 by Student's t test. (F) Quantification of neuritic plaques in APP23/PS45 mice with treatment starting at the age of 6 wk, the number represents mean ± SEM. n = 25 mice for control and 29 mice for VPA. *, P < 0.0001 by Student's t test.