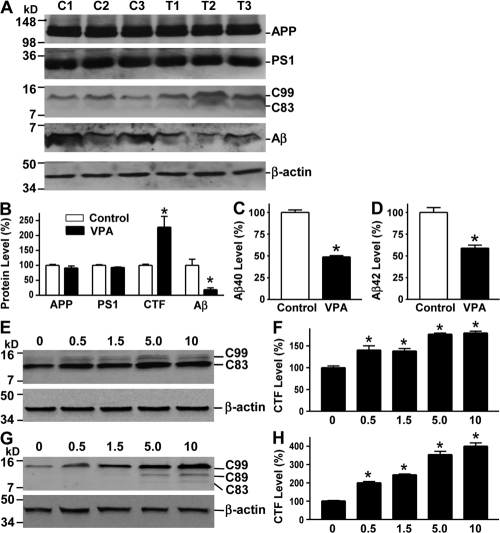
Figure 3.
VPA inhibits γ-secretase cleavage of APP and Aβ production. (A) Half brains from VPA-treated and control APP23 mice of the 7-mo age group were lysed in RIPA-Doc lysis buffer and separated with 16% Tris-Tricine SDS-PAGE. APP full-length and CTFs (C99 and C83) were detected by C20 polyclonal antibody. PS1 was detected by anti-PS1 N-terminal antibody 231. Total Aβ was isolated from the brain tissues with 4G8 monoclonal antibody and detected using 6E10 anti-Aβ monoclonal antibody. β-Actin was detected by anti–β-actin antibody AC-15 as the internal control. (B) Quantification showed that CTFs were significantly increased, whereas Aβ levels were markedly reduced in VPA-treated mice. n = 30 each for control and VPA group. *, P < 0.05 by Student's t test. ELISA assay was performed to measure Aβ40 (C) and Aβ42 (D) levels in the conditioned media of primary neuronal cultures derived from the brain tissues of newborn APP23/PS45 mice. The cells were cultured for a week before VPA treatment for 24 h. n = 3. *, P < 0.005 by Student's t test. (E) Swedish mutant APP stable cell line 20E2 was cultured and treated with different doses of VPA for 24 h, and cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis. C99 and C83 were detected with C20 antibody. β-Actin was detected by anti–β-actin antibody AC-15 as the internal control. (F) Quantification of CTF (C99 and C83) generation in 20E2 cells. VPA treatment significantly increased APP CTF production. n = 4. *, P < 0.001 by ANOVA. (G) APP C99 stable cell line H99C1 was treated with different doses of VPA for 24 h, and the CTFs (C99, C89, and C83) were detected by 9E10 antibody. β-Actin was detected by anti–β-actin antibody AC-15 as the internal control. (H) Quantification of CTFs (C99, C89, and C83) levels in H99C1 cells. VPA treatment significantly increased APP CTF production. n = 4. *, P < 0.001 by ANOVA.