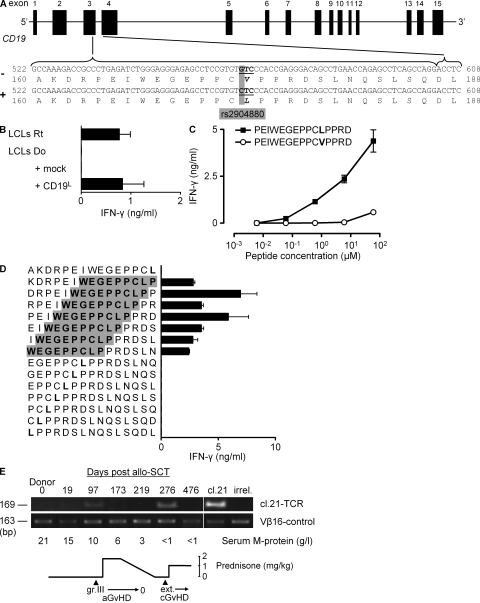
Figure 2.
CD19L encodes for the mHag recognized by clone 21. (A) The CD19 gene with rs2904880 in the third exon encoding a valine (V) to leucine (L) substitution at position 174. (B) IFN-γ response of clone 21 to mHag− donor (Do) EBV-LCLs transduced either with an empty vector (mock) or with the CD19L-encoding vector. Response to mHag+ recipient (Rt) EBV-LCLs (LCLs) is depicted as positive control. The mean and SEM of three experiments are depicted. (C and D) IFN-γ response of clone 21 toward serial concentrations of 15-mer peptides derived either from CD19L (▪) or from CD19V (○; C) or toward CD19L-derived overlapping 15-mer peptides (D). Donor EBV-LCLs were used as APCs. The core sequence recognized by clone 21 is highlighted in gray. Error bars represent the SEM of triplicate cultures. (E) In vivo presence of CD19L-specific clone 21. Genomic DNA isolated from patient PBMCs at the indicated days after allo-SCT was used to amplify the TCR of clone 21. Vβ16-specific PCR was used as positive control. Genomic DNA from clone 21 (cl.21) and third-party PBMCs (irrel.) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Also indicated are the severity of acute and chronic GvHD, the serum M protein levels, and the immunosuppressive prednisone treatment during the monitoring period.