Table 1.
Relative kinetic (kRH/kR′H) and thermodynamic (KRH/R′H) selectivity of C–H bond activation for substrates RH by complex 1.
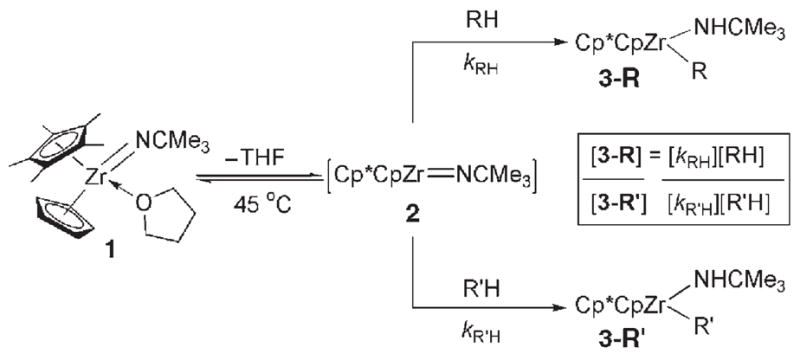 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-R[a] | RH | kRH/kR′H[b] | KRH/R′H[c] | 3-R[a] | RH | kRH/kR′H[b] | KRH/R′H[c] |
| 3 a |
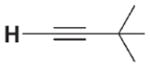
|
>106 | n.d.[d] | 3 f |
|
17 | 170 |
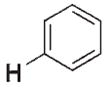
| 3 b |
|
700 | 370 | 3 g |
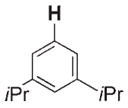
|
16 | 160 |
| 3 c |
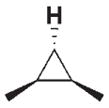
|
280 | 40 | 3 h |
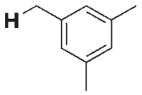
|
15 | 30 |
| 3 d |
|
220 | 750 | 3 i |
|
1.7 | 1 |
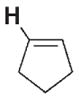
| 3 j |
|
1.5 | n.d.[d] | ||||
| 3 e |
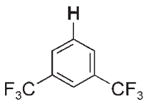
|
36 | 26 000 | 3 k |
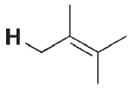
|
1 | 0.6[e] |
Products 3-R formed from 1 and the explicitly drawn C–H bond in the corresponding substrate RH.[8]
Relative rates (kRH/kR′H) for RH activation by 1 calculated per reactive RH bond at 45°C; kR′H = kRH for 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene.
Relative thermodynamic stability (KRH/R′H) of products 3-R relative to 3 i measured at 150°C from 1 and calculated per reactive RH bond.
Determination of thermodynamic selectivity was unsuccessful owing to decomposition of 3-R. [e] Thermodynamic selectivity measured at 105°C.
