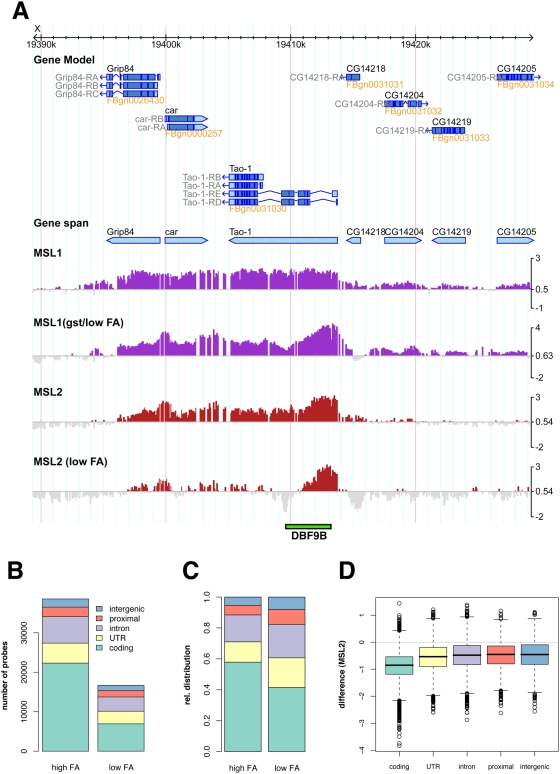
Figure 2. Differential crosslinking alters the binding patterns and improves mapping of high-affinity sites.
A) Genome browser snapshot with gene spans and gene models. MSL1 and MSL2 profiles after low or high formaldehyde (FA) crosslinking are depicted as the log2 of the mean enrichment ratio (IP/Input) of at least 2 replicate experiments. The Tao-1 gene contains a confirmed HAS (DBF 9B), which is indicated by the green box below the profiles. B) Absolute changes in numbers of probes significantly bound by MSL2 after differential crosslinking. C) Corresponding relative changes according to functional context. D) Changes in MSL2 signals on MSL2 target probes grouped according to genomic context when crosslinking under low FA conditions compared to high FA crosslinking.