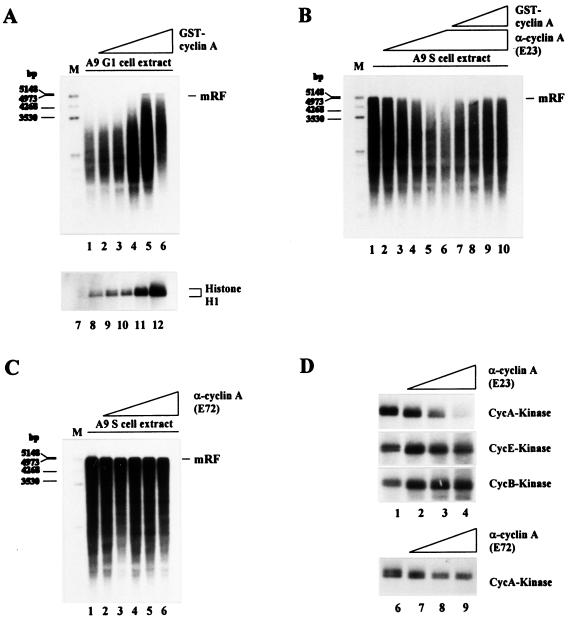
Figure 3.
Effect of cyclin A on the ability of A9 cell extracts to convert MVM ss DNA into RF. (A) MVM ss DNA (20 ng) was incubated in G1 cell extract alone (80 μg) (lane 1) or in the presence of 0.1 μg (lane 2), 0.2 μg (lane 3), 0.4 μg (lane 4), 0.6 μg (lane 5), or 0.8 μg (lane 6) of GST-cyclin A. Cyclin A-dependent kinase activity was determined by phosphorylation of histone H1 after addition of increasing amounts of GST-cyclin A (0.0 μg, lane 7; 0.1 μg, lane 8; 0.2 μg, lane 9; 0.4 μg, lane 10; 0.8 μg, lane 11; 1.6 μg, lane 12) to G1 cell extract samples (80 μg protein) and cyclin A/cdk complex immunoprecipitation. (B) MVM ss DNA (20 ng) was incubated in S cell extract alone (lane 1) or in the presence of 0.4 μg (lane 2), 0.8 μg (lane 3), 1.2 μg (lane 4), 1.6 μg (lane 5), or 2.0 μg (lanes 6 to 10) of the cyclin A-specific neutralizing mAb E23 and additionally 0.2 μg (lane 7), 0.4 μg (lane 8), 0.8 μg (lane 9), or 1.2 μg (lane 10) of GST-cyclin A. (C) MVM ss DNA (20 ng) was incubated in S cell extract alone (lane 1) or in the presence of 0.4 μg (lane 2), 0.8 μg (lane 3), 1.2 μg (lane 4), 1.6 μg (lane 5), or 2.0 μg (lane 6) of the cyclin A-specific nonneutralizing mAb E72. (D) Samples (80 μg protein) from S cell extract were supplemented with increasing amounts of the cyclin A-specific Abs E23 or E72 (no Ab, lanes 1 and 6; 0.6 μg, lanes 2 and 7; 1.2 μg, lanes 3 and 8; 1.8 μg, lanes 4 and 9), and kinase activities were determined as described in Materials and Methods. mRF, monomer replicative form DNA; M, size markers in bp.