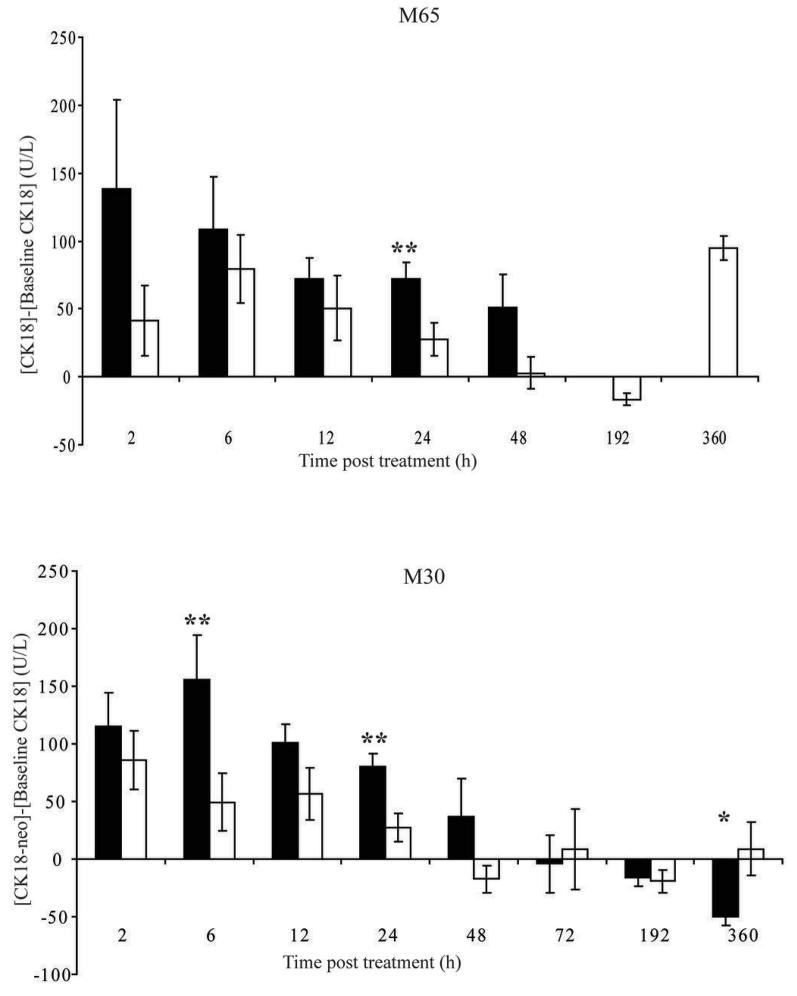
Figure 4. Levels of circulating CK18 (M65) [A] and CK18-neo (M30) [B] in H146 SCLC human xenograft bearing mice treated with either ABT-737 or vehicle.
Female age and sex-matched SCID/bg mice were implanted with H146 SCLC cells until the tumours reached ∼400 mm3, at which point animals received either daily ABT-737 at 100 mg/kg/day via i.p. administration (black bars) or vehicle (white bars) and terminal bleed plasma samples were taken and assayed for A. intact CK18 and B. cleaved CK18 using M65 and M30 assays, respectively. Levels of CK18 or cleaved CK18 were calculated by subtraction of baseline levels taken 24 hours prior to dosing via retro-orbital survival bleed. Data are from 10 (6, 12, 24 and 192 h), 7 (2 h) or 3 (48, 72 and 360 h) ABT-737-treated mice per group and 10 (6, 12, 24 and 192 h), 7 (2 h) or 3 (48, 72 and 360 h) vehicle control treated mice plotted as mean ± SEM. p<0.05 (*); p<0.01 (**).