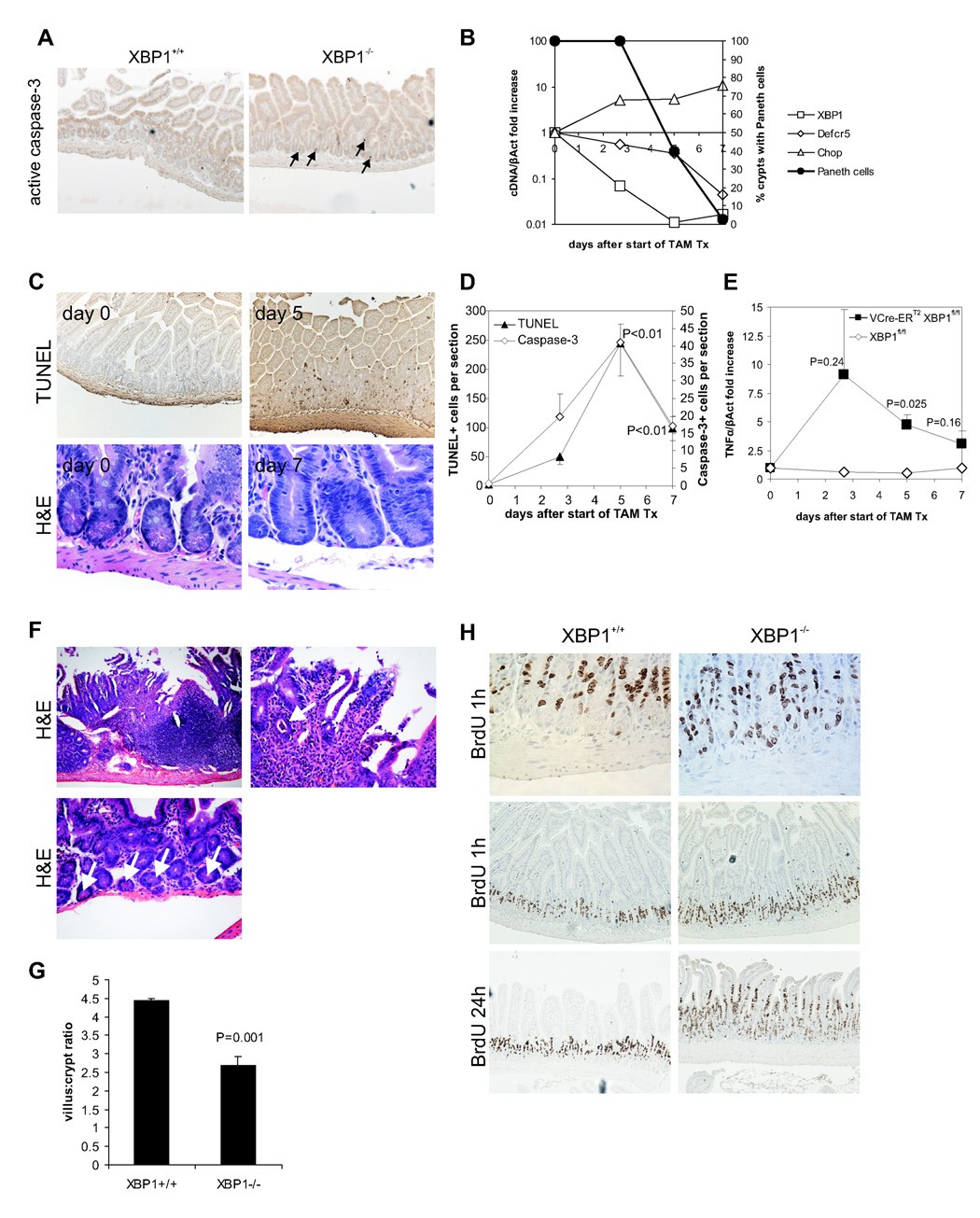
Figure 2. XBP1 deletion results in apoptotic Paneth cell loss, inflammation, a distorted villus:crypt ratio, and IEC hyperproliferation.
A. Apoptotic nuclei were identified in XBP1+/+ (XBP1flox/floxVCre) and XBP1−/− (XBP1flox/flox) sections with anti-active (cleaved) caspase-3. Arrows point to apoptotic cells. B. XBP1floxneo/floxneoVCre-ERT2 mice were administered 5 daily doses of 1 mg tamoxifen to induce deletion of the XBP1floxneo gene in the intestinal epithelium. XBP1, cryptdin-5 (Defcr5), and Chop mRNA (all expressed normalized to β-actin; left y axis) expression in epithelium during and after tamoxifen treatment. Percentage of crypts with Paneth cells on H&E staining is shown (right y axis). Representative experiment of 3 performed. C. TUNEL and H&E staining on small intestinal sections of tamoxifen-treated XBP1floxneo/floxneoVCre-ERT2 mice collected at the indicated days. D. TUNEL+ and caspase-3+ cells were enumerated by light microscopy (3 mice per time-point with ileal and jejunal sections each; P values indicate comparisons to time-point 0; Student’s t test). E. TNFα mRNA was quantified by qPCR in small intestinal epithelial scrapings from ileum harvested at the indicated time-points after start of tamoxifen administration from VCre-ERT2 XBP1floxneo/floxneo (n = 4 per time-point) or XBP1floxneo/floxneo (n = 1 per time-point) mice. P values indicate comparisons to time-point 0; Student’s t test. F. Enteritis in the small intestine in VCre-ERT2 XBP1floxneo/floxneo mice on day 5 after TAM administration. Upper left panel, 100×; upper right panel, same section, 400×, arrow points to a crypt abscess; lower panel 100×, crypts with Paneth cells (arrows). G. Jejunal sections of XBP1flox/flox (XBP1+/+; n = 7) and XBP1flox/floxVCre (XBP1−/−; n = 8) mice were assessed for their villus:crypt ratio on H&E stainings (ratios of ≥ 4:1 are considered normal for jejunum). H. XBP1flox/flox (XBP1+/+) and XBP1flox/floxVCre (XBP1−/−) mice were administered bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) i.p., and small intestinal sections harvested after 1 h and 24 h (n = 3 per genotype per time-point). The 1 h time-point labels the pool of proliferating IEC in the crypts (mostly transit amplifying IEC), whereas the 24 h time-point assesses the migration along the crypt-villus axis indicating the turn-over of the IEC compartment.