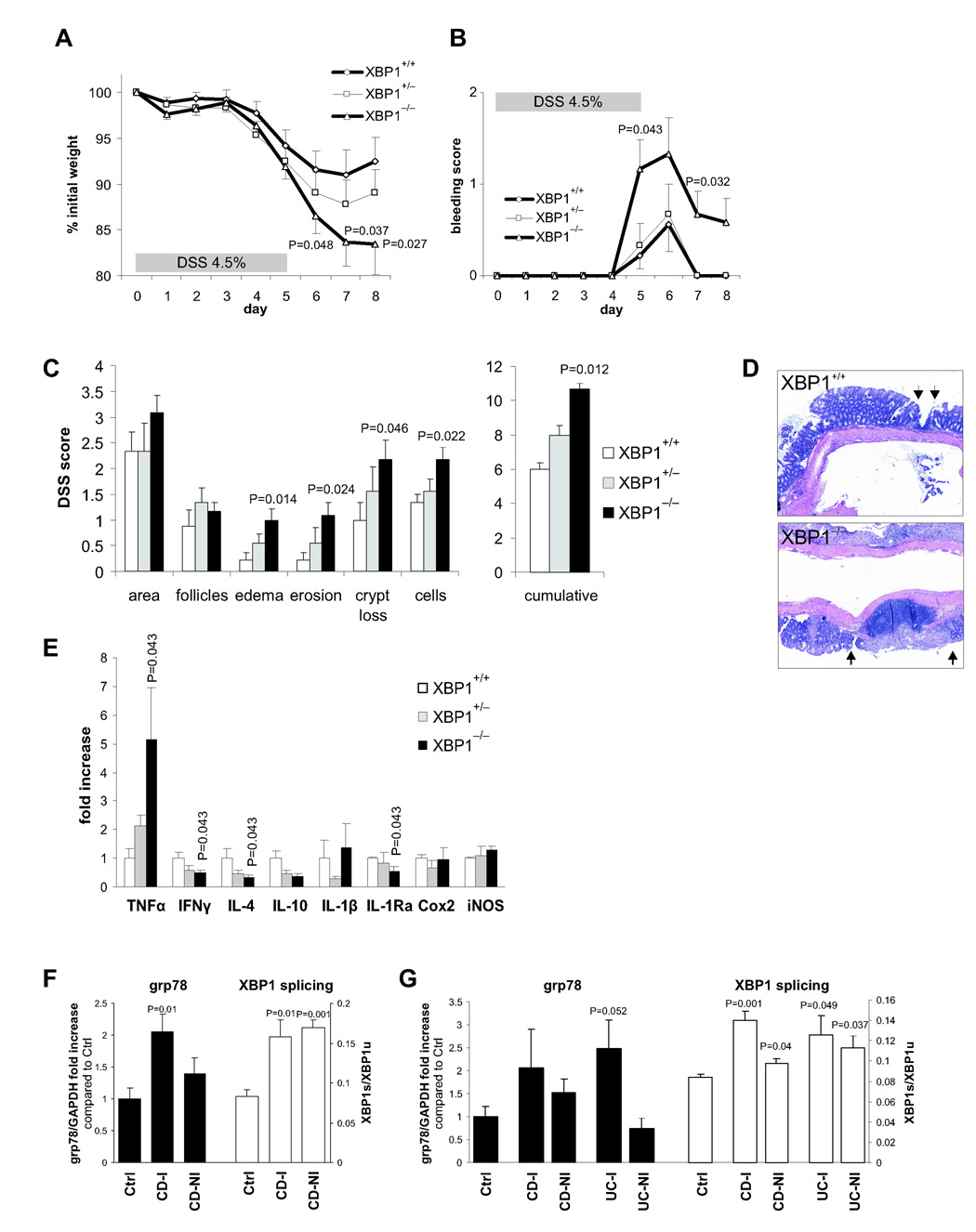
Figure 5. XBP1 deficiency increases susceptibility to DSS colitis.
A. 4.5% DSS was administered in drinking water for 5 days and then replaced by regular drinking water in XBP1+/+ (n = 9), XBP1+/− (n = 9) and XBP1−/− (n = 12) littermates (age 6–12 weeks). Wasting is presented as % of initial weight. One-tailed Student’s t test was performed. B. Presence of rectal bleeding during DSS colitis was assessed daily and scored as in Methods. Mean ± s.e.m.; XBP1+/+ (n = 9), XBP1+/− (n = 9) XBP1−/− (n = 12). Two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was peformed. C. Individual signs of inflammation of colonic tissue harvested on day 8 of DSS colitis were scored blindly. Two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was performed. D. Typical colonic histology on day 8 of DSS colitis. Arrows, borders of ulcers. E. mRNA expression (normalized to βactin) of inflammatory mediators was quantified by qPCR in colonic specimens on day 8 of DSS colitis. n = 4 per group. Mean ± s.e.m analyzed by two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. F. Human ileum in Crohn’s disease exhibits signs of ER stress. Inflamed (“CD-I”, n = 3) and non-inflamed (“CD-NI”, n = 3) ileal biopsies from CD patients and healthy control (“Ctrl”, n = 4) subjects were analyzed for grp78 mRNA expression (levels in Controls were arbitrarily set at 1, and CD-I and CD-NI levels expressed as ratio to Controls; left y axis). XBP1 mRNA splicing is expressed as ratio of XBP1s/XBPu (right y axis). G. Human colon mucosa in Crohn’s disease (“CD”) and ulcerative colitis (“UC”) exhibits signs of ER stress. Colonic biopsies from inflamed (“−I”) and non-inflamed (“−NI”) CD and UC patients (n = 3 each) and healthy control subjects (“Ctrl”, n = 4) were analyzed for grp78 mRNA expression and XBP1 splicing as described in (F).