Fig. 5.
In vitro translocation assay with isolated inverted inner membrane vesicles of E. coli.
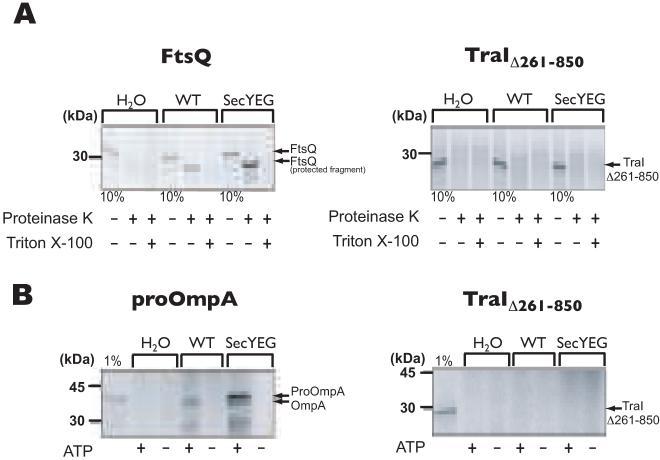
A. FtsQ and TraIΔ261-850 were used in a co-translational targeting/transport assay in which the translocation into inverted inner membrane vesicles was monitored by the accessibility of the transported protein to externally added proteinase K, in the presence or absence of Triton X-100. To detect even small amounts of transported protein, inverted membrane vesicles derived from a strain overexpressing the SecYEG translocase were also used. Ten (10) % of the reaction mixture before addition of proteinase K was loaded as a synthesis control. FtsQ is a membrane protein whose insertion into the vesicles is mediated by Sec proteins. Only a small domain of FtsQ is exposed on the outside of the vesicles and is accessible to degradation by proteinase K.
B. proOmpA and TraIΔ261-850 were used in a post-translation protein transport assay in the presence or absence of inner membrane vesicles, as described above, with or without ATP. One (1) % of synthesized protein before addition of proteinase K was loaded as a control. proOmpA contains a signal peptide for transport into the periplasm and is processed by leader peptidase.