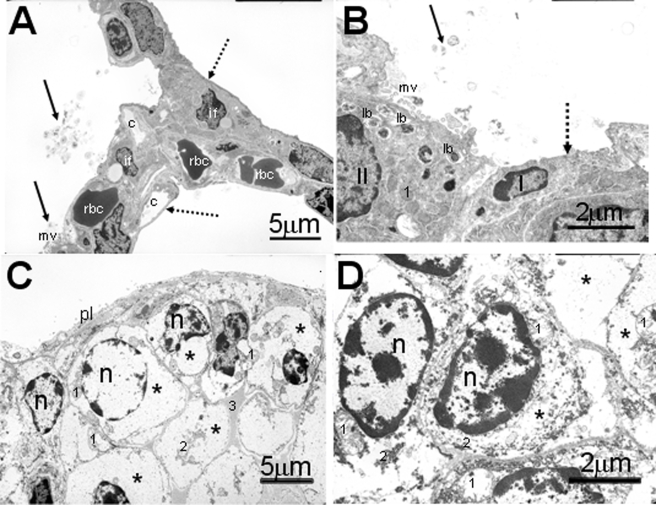
FIGURE 4.
Electron photomicrographs of alveolar epithelium of newborn pups. The lung from the control pup (A and B) has a well differentiated alveolar epithelium containing both type I and II cells (B). Stippled arrow indicates thin, squamoid, type I cells, and solid arrows indicate tubular myelin figures (secreted surfactant) within the alveolar airspace of control pup. Type II cells have numerous intracytoplasmic lamellar bodies (lb) and apical microvilli (mv). In contrast the alveolar surface in HIF1αΔ/Δ pup (C and D) is lined by large undifferentiated cuboidal epithelial cells. The cytoplasm of these epithelial cells are primarily filled with glycogen (*). No lamellar bodies are present in these cells. c, capillary; rbc, red blood cells; II, type II alveolar epithelial cell; I, type I alveolar epithelial cell; if, interstitial fibroblast; *, glycogen; n, nucleus; 1, mitochondrion; 2, rough endoplasmic reticulum; pl, pleural surface; solid black arrows, tubular myelin; stippled arrow, type I cells. All doxycycline treatments were at least 12 days.