Figure 2.
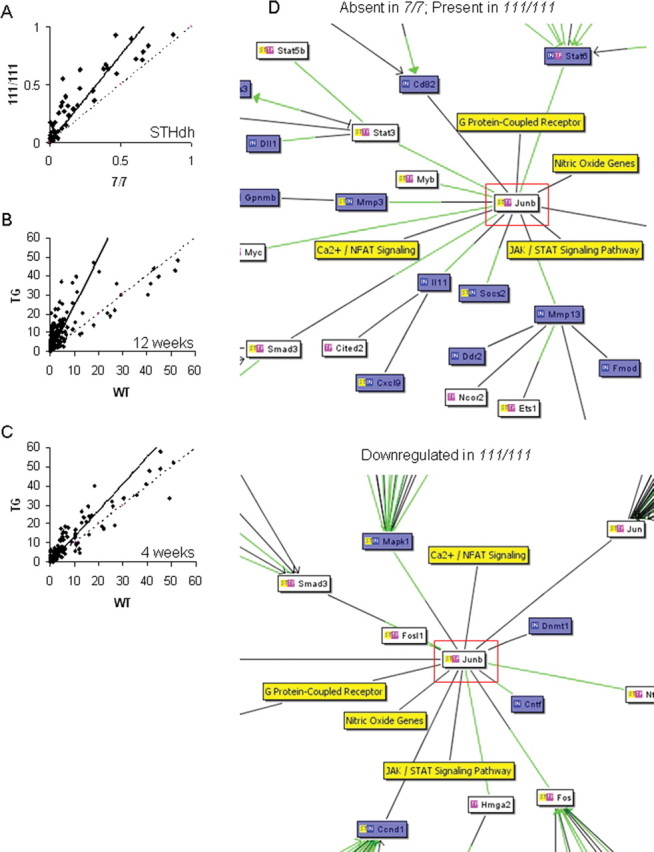
Mutant Htt alters the binding of many transcription factors. Densitometric analyses of transcription factor binding activity are scatter plotted, with each point representing the correlation of the binding activity of each transcription factor in two different conditions. Dashed line indicates the predicted correlation if there is no difference in binding activities between the two conditions, whereas the solid line indicates the actual correlation. A, Transcription factor binding activities are increased in the homozygote STHdh111/111 compared with STHdh7/7 cells (measured by film densitometry). B, C, The progressive increase in binding of many transcription factors at 12 weeks in the R6/2 transgenic mouse striatum (B) is evident at the presymptomatic age of 4 weeks (C). D, Increased transcription factor activity does not have straightforward effects on gene expression profiles (Table 1), but correlates well with gene expression changes. Interaction networks from cocitation literature mining generated by the Bibliosphere Pathway view (Genomatix) display the relationship of transcription factors (white boxes), mRNA expression levels (blue boxes), and expression pathways (yellow boxes). The green lines represent a binding site for the relevant transcription factor on the gene promoter. Shown are part of the interaction networks for JunB (highlighted in red), demonstrating different interactions in STHdh7/7 and STHdh111/111 cell lines. JunB exerts two types of gene expression effects (top, mRNA absent in STHdh7/7 and present in STHdh111/111 cells; bottom section shows part of an interaction network for mRNA present in both cell lines but downregulated in STHdh111/111 homozygotes). Full interaction networks generated by the Bibliosphere Pathway view (Genomatix) for each of the four lists of genes are shown in supplemental Figure 1 (available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). JAK, Janus kinase; Fmod, fibromodulin; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.
