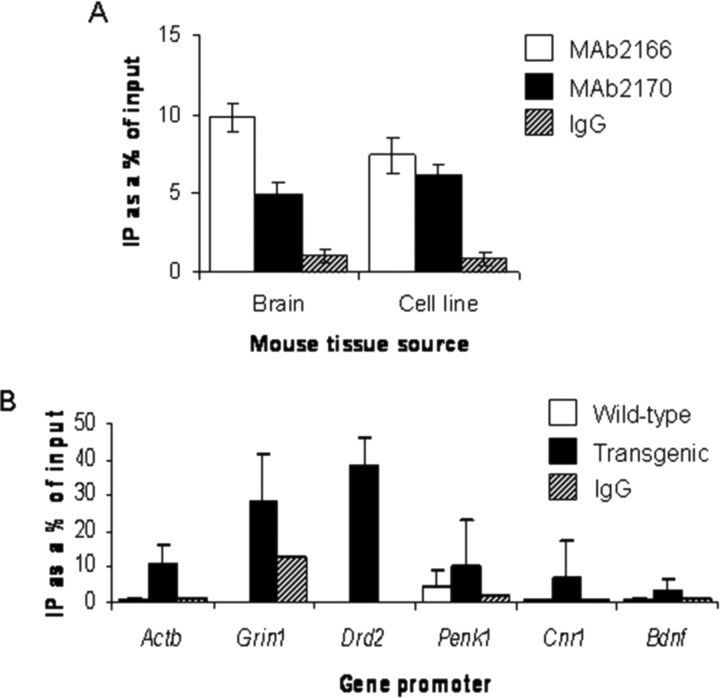
Figure 3.
Htt-gene-promoter occupancy is modulated by polyQ repeat length. A, DNA quantitation of ChIP using different Htt antibodies in wild-type brain and cell lines. MAb2166 (open bars) and MAb2170 (filled bars) compared with IgG or no antibody (hatched bars) shows that significant amounts of DNA are pulled down. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 3–4). B, ChIP with the MAb2170 Htt antibody in R6/2 mouse brain reveals nonselective increases in Htt-promoter occupancy in transgenic mice (filled bars) compared with wild-type mice (open bars), including those for genes whose expression is unchanged [Actb (β-actin) and Grin1 (NMDA receptor NR1 subunit)], and those for genes downregulated in HD [Drd2 (dopamine D2 receptor), Penk1 (preproenkephalin), Cnr1 (cannabinoid receptor 1), and Bdnf (brain derived neurotrophic factor), which is not expressed in striatal neurons]. Hatched bars represent negative control conditions. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 2–4).