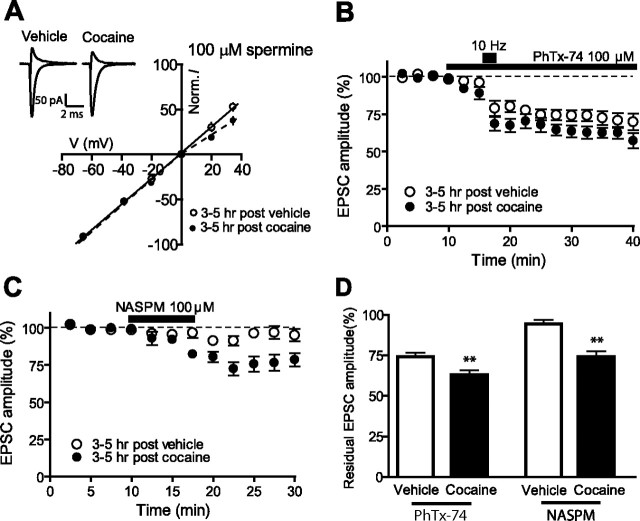
Figure 5.
Brief exposure to cocaine triggers the insertion of GluR2-lacking AMPARs on VTA neurons within 3–5 h. A, Average I–V plots from slices exposed 3–5 h earlier to vehicle (n = 11) or cocaine (n = 7). A, Inset, Representative traces recorded at −70 mV and +40 mV in the presence of d-APV (50 μm) and with spermine (100 μm) in the internal solution. B, D, Time course of EPSC amplitudes showing the effect of PhTx-74 (100 μm, 30 min) on VTA neurons exposed 3–5 h earlier with cocaine (n = 8) or vehicle (n = 8) (B) and summary of residual EPSCs measured 20–25 min after drug perfusion (D). The short bar in B indicates the period of high-frequency stimulation (10 Hz, 2 min) that allows binding of the toxin to the open conformation of AMPA channels. C, D, Time course of EPSC amplitudes showing the effect of NASPM (100 μm, 7.5 min) on VTA neurons exposed 3–5 h earlier with cocaine (n = 7) or vehicle (n = 7) (C) and summary of residual EPSCs measured 15–20 min after drug perfusion (D). Norm., Normalized. **p < 0.01. Error bars represent SEM.