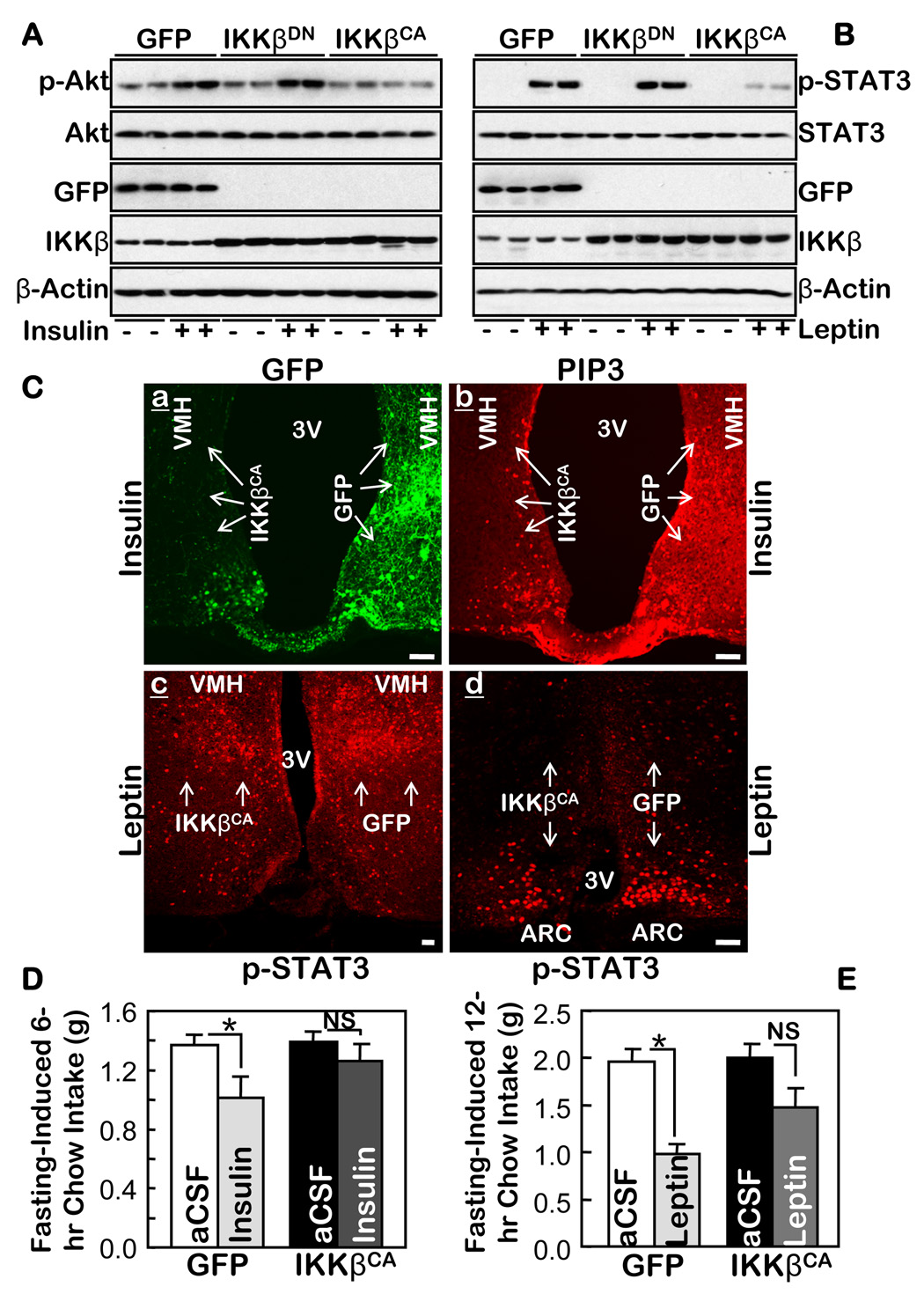
Figure 4.
IKKβ/NF-κB in the MBH mediates central insulin and leptin resistance. A & B. An adenovirus was injected to deliver IKKβCA, IKKβDN, or GFP to both MBH sides of normal C57BL/6 mice. Following surgical recovery, 24-hour-fasted mice received third-ventricle injections of either insulin (A) or leptin (B) (+), or the empty vehicle (−) (A & B). Proteins in the dissected hypothalamus were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. C. Adult C57BL/6 mice were injected with adenoviruses to deliver IKKβCA into one side of the MBH and GFP into the other side (a) of the same mice. Recovered mice were fasted 48 hours and then stimulated with insulin (a–b) or leptin (c–d) for 20 min via a third-ventricle cannula. Brain sections across the MBH were directly examined for GFP (a), and immunostained with the indicated primary antibodies (b–d). Arrows indicate the regions in which the injected genes (IKKβCA and GFP) were expressed. Bar = 100 µm. D & E. An adenovirus was injected into adult C57BL/6 mice to deliver either IKKβCA to both sides of the MBH of one group of mice or GFP to both sides of the MBH of another group of mice. Recovered mice fasted for 4 hours received third-ventricle injections of insulin (D), leptin (E), or the vehicle (aCSF) (D & E). Food intake during the indicated time periods following the insulin or leptin injections was measured. (Insulin: n = 12 per group; Leptin: n = 7–8 per group; *p<0.05). NS = non significant.