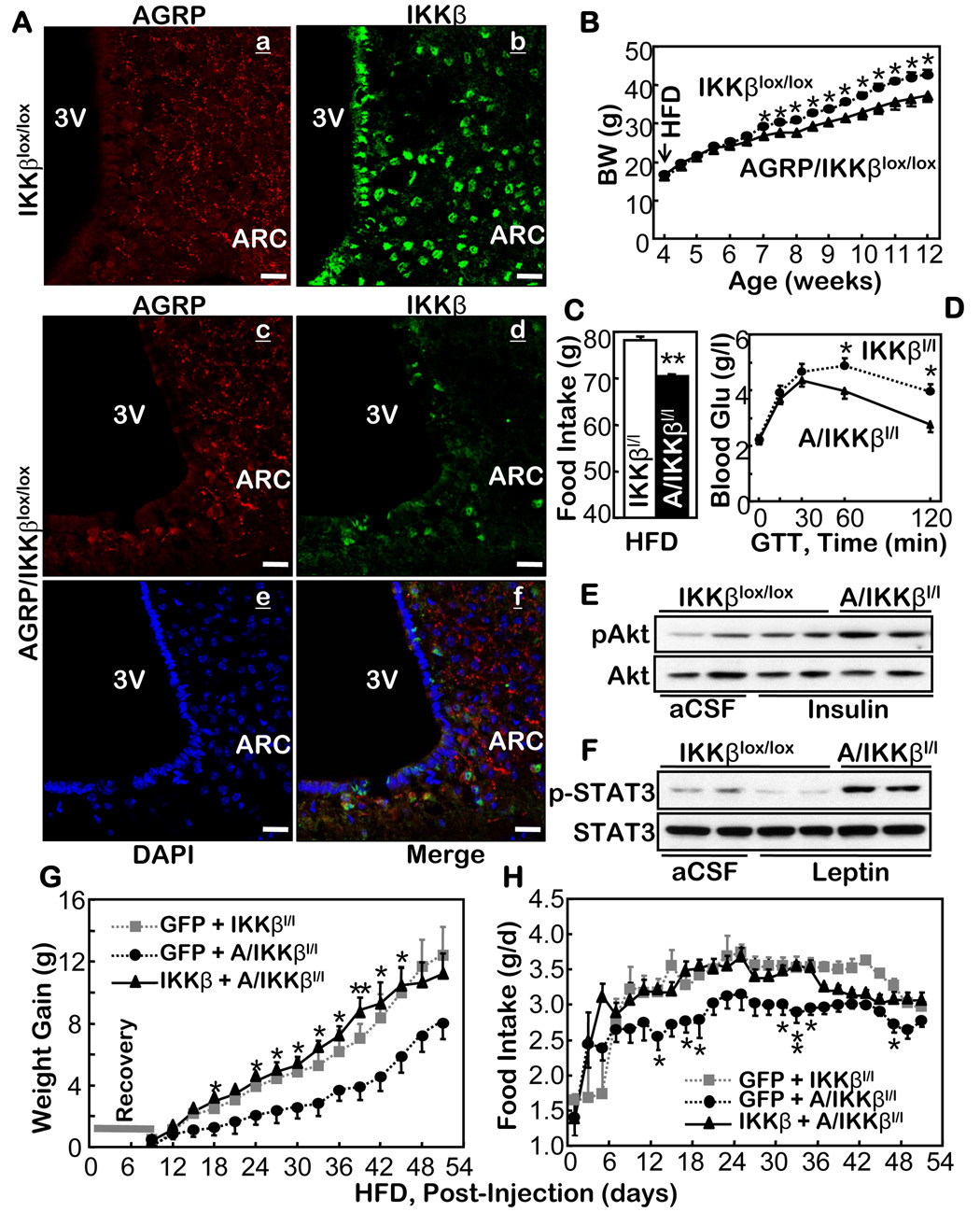
Figure 5.
Anti-obesity effects of knocking out IKKβ in the hypothalamic AGRP neurons. A. AGRP (a & c) and IKKβ (b & d) in the hypothalamus of the control mice (IKKβlox/lox mice) (a & b) vs. AGRP-IKKβlox/lox mice (c & d) were immunostained. Immunostaining of AGRP (c) and IKKβ (d) and the nuclear staining by DAPI (e) in the hypothalamus of AGRP-IKKβlox/lox mice were merged to display the absence of IKKβ in AGRP neurons (f). Bar = 25 µm. B–D. Body weight (BW) (B), HFD intake (C), and glucose tolerance (GTT) (D) were tested in HFD-fed AGRP-IKKβlox/lox mice and IKKβlox/lox mice. (n = 12–14 per group, *p<0.05). Glu, Glucose. E & F. HFD-fed AGRP-IKKβlox/lox mice and IKKβlox/lox mice were fasted and received third-ventricle injections of insulin (5 mU) (E), leptin (10 µg) (F), or the vehicle (aCSF) (E & F). Insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation (pAkt) (E) and leptin-induced STAT3 phosphorylation (pSTAT3) (F) were determined using Western blots. G & H. Adenovirus was injected to deliver IKKβ to the both MBH sides of AGRP-IKKβlox/lox mice. For the controls, adenovirus was injected to deliver GFP to the both MBH sides of AGRP-IKKβlox/lox mice and to the both MBH sides of IKKβlox/lox mice. Body weight (G) and food intake (H) in these mice were followed for 8 weeks following the viral injections (n = 5 per group; **p<0.01). C–H. IKKβl/l: IKKβlox/lox mice; A/IKKβl/l: AGRP-IKKβlox/lox mice.