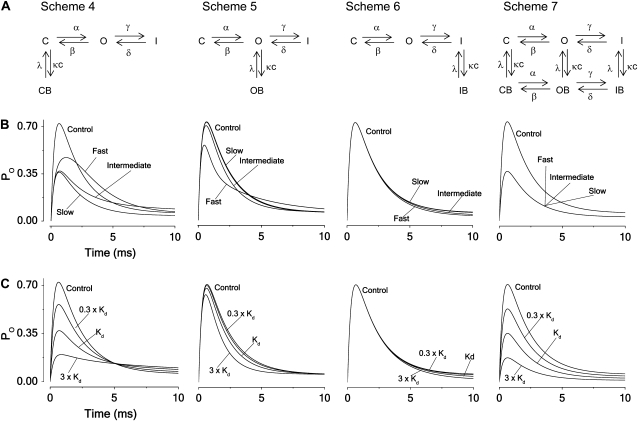
FIGURE 2.
Principal blocking mechanisms of an inactivating channel. (A) Kinetic schemes. Symbols as in Fig. 1. I denotes an inactivated state of the unbound channel and IB the inactivated state of the local anesthetic bound channel; γ and δ denote the inactivation rate constants and c the local anesthetic concentration. (B) Computed time courses of the current for the different block schemes. Calculated for Kd concentration from Eqs. 3–5, assuming V = +60 mV and using parameter values in Table 1 (Shaker) for fast, intermediate, and slow blocking rates (κ = λ = 1, 0.1, and 0.01 ms−1). (C) Computed time courses of the open probability for the different schemes at concentrations 0.3 × Kd, Kd, and 3 × Kd, assuming intermediate blocking rates (κ = 0.1 and λ = 0.1 ms−1).