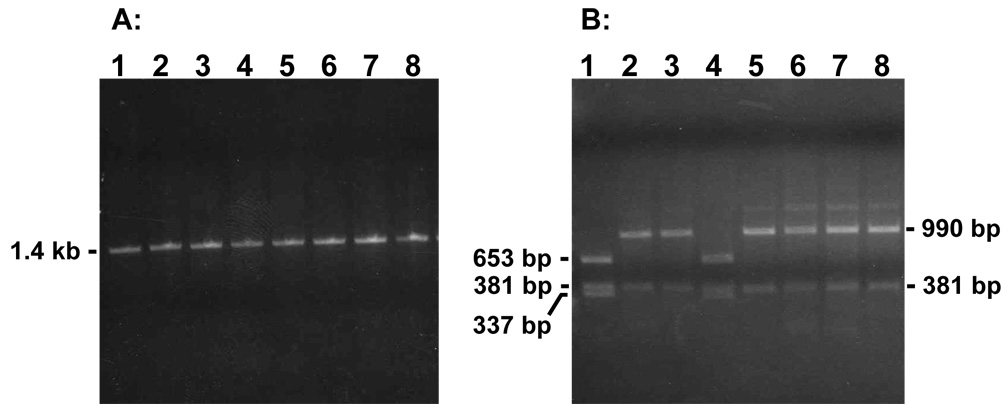
Fig. 3.
Representative analysis of PCR products from G418R segregants. (A) Using primers AW85 and AW91, PCR products were generated from genomic DNA samples isolated from parental cell line pLB4/11 (lane 1) or representative G418R segregants arising from pLB4/11 (lanes 2–8) following treatment with RTX. (B) Lanes 1–8 display the PCR products from the corresponding lanes in (A) following digestion with AluI. The digested PCR product from parental cell line pLB4/11 in lane1 illustrates the nonrecombinant pattern of restriction fragments. The clone displayed in lane 4 produced a nonrecombinant pattern, while the remaining clones each produced the expected recombinant AluI digest pattern. Although not shown, for the gels in (A) and (B) a HindIII digest of lambda DNA and a HaeIII digest of phi X DNA were also run as molecular weight markers to confirm PCR fragment sizes.