Fig. 1.
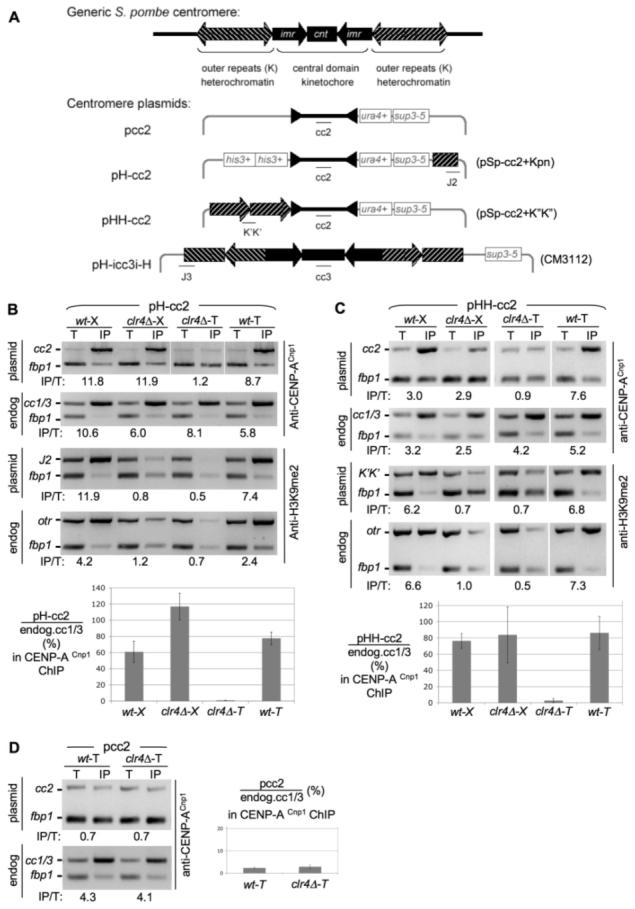
Testing roles for Clr4 in establishment of CENP-ACnp1 chromatin at centromeres. (A) Fission yeast centromere DNA and minichromosomes used (20). Association of CENP-ACnp1 and H3K9me2 with pH-cc2 (B), pHH-cc2 (C), or pcc2 (D) introduced into wild-type (wt) or clr4 cells by crossing (X) or transformation (T) is shown (see also fig. S1). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product positions on minichromosomes are indicated (A). fbp1 is the control noncentromeric locus. In CENP-ACnp1 ChIP, enrichment of pcc2 product was compared with input DNA (T) relative to fbp1. Enrichment of endogenous cc1/3 relative to fbp1 was also assessed. In H3K9me2 ChIP, enrichment at plasmid–outer repeats J2 (B) or K″K″ (C) products was compared with the PCR of input DNA relative to the fbp1 product. Enrichment of endogenous otr sequences was also assessed (B and C). Quantitative PCR confirms these results [lower panels (B) and (C) and right (D) and fig. S3] (20). Histograms show percent enrichment on plasmid relative to endogenous cc1/3.
