Figure Figure 4.
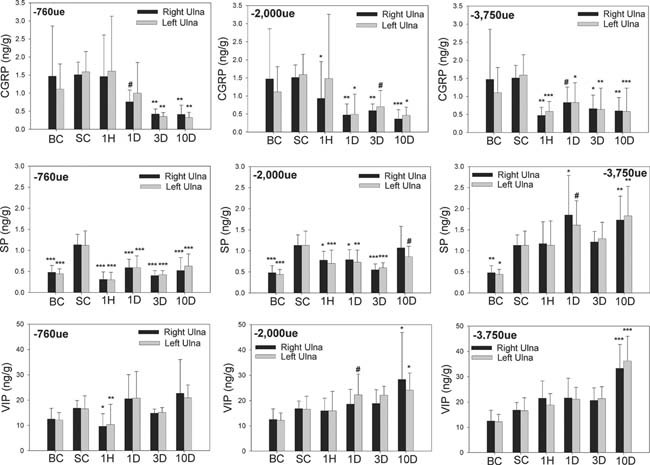
Unilateral cyclic loading of the right ulna induced persistent changes in bone neuropeptide concentrations in both the loaded (right) ulna and the contralateral (left) ulna. Unilateral cyclic loading of the right ulna induced bilateral decreases in ulnar CGRP concentrations that persisted for the 10‐day experimental period. Loading with low and medium initial peak strain also induced similar changes in ulnar SP concentrations; these effects were not evident with high strain loading. Ulnar VIP concentrations were also increased bilaterally at 10 days in response to loading at high strain. The Sham control group was not significantly different from the baseline control group for CGRP and VIP, whereas bone concentrations of SP were increased in the Sham control group. BC, baseline control; SC, Sham control; 1H, 1 h after loading; 1D, 1 day after loading; 3D, 3 days after loading; 10D, 10 days after loading; −760 μϵ, loading at low initial peak strain using −3.3 N; −2000 μϵ, loading at medium initial peak strain using −10 N; −3750 μϵ, loading at high initial peak strain using −18 N. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; # p < 0.15 vs. the relevant Sham control. Error bars represent SD. Loaded groups, n = 12; Sham control group, n = 9; baseline control group, n = 12.
