Fig. 2.
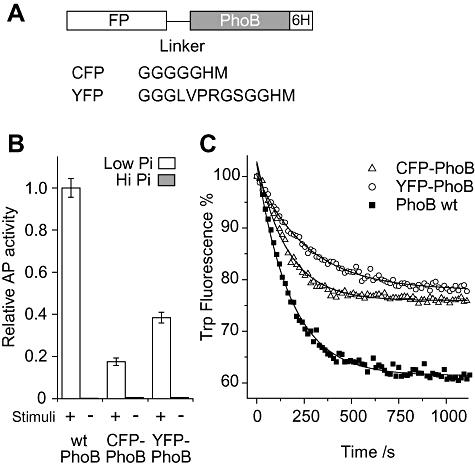
Alkaline phosphatase (AP) assays and in vitro phosphorylation of FP–PhoB hybrids.
A. Diagram of FP–PhoB proteins. Different flexible linkers are engineered between PhoB and different FPs. For YFP–PhoB, an arginine residue in the linker makes it susceptible to trypsin digestion. All FP–PhoB proteins have a His6 tag for purification.
B. Expression of AP. A phoB deletion strain carrying either pRG20 (CFP–PhoB) or pRG94 (YFP–PhoB) and the wild-type strain BW25113 were assayed for AP activity under low-phosphate (Pi) (white) and high-Pi (grey) conditions. FP–PhoB hybrids were induced by IPTG to an expression level of protein comparable to that of wild-type PhoB. The data are from three replicates. Protein expression levels were confirmed to be comparable by Western blot analyses (data not shown).
C. Tryptophan fluorescence quenching upon phosphorylation. Tryptophan fluorescence of individual PhoB proteins (2 μM) was monitored at the emission wavelength of 345 nm with the excitation at 295 nm. Proteins include CFP–PhoB (open triangle), YFP–PhoB (open circle) and PhoB (solid squares). These proteins were mixed with 20 mM phosphoramidate in the reaction buffer and the phosphorylation was initiated by addition of MgSO4 to a final concentration of 5 mM. Solid lines represent the fitted exponential decay curves. Three repeated experiments gave the average rate constants as: CFP–PhoB, 6.6 ± 0.6 × 10−3 s−1; YFP–PhoB, 3.5 ± 0.4 × 10−3 s−1; PhoB, 5.6 ± 0.6 × 10−3 s−1.
