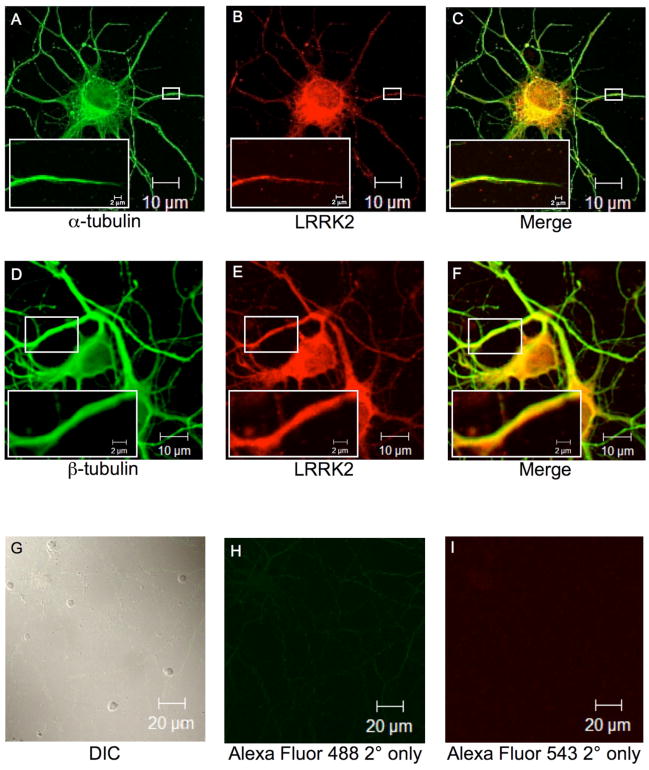
Fig. 4. Endogenous LRRK2 co-localizes with α/β-tubulin in primary hippocampal neurons.
Cultured embryonic rat hippocampal neurons were used for immunofluorescence microscopy. Neuronal cells were immunostained with respective primary antibodies followed by labeling with fluorophore-tagged secondary antibodies. Fluorescence images were analyzed by inverted laser-scanning confocal microscopy. (A). α-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibody primary staining followed by Alexa Flour GAM-488 secondary staining. (B) LRRK2 rabbit polyclonal antibody primary staining followed by Alexa Flour GAR-543 secondary staining. (C) Digitally merged image of Panels A and B. (D). β-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibody primary staining followed by Alexa Flour GAM-488 secondary staining. (E) LRRK2 rabbit polyclonal antibody primary staining followed by Alexa Flour GAR-543 secondary staining. (F) Digitally merged image of Panels D and E. Small white boxes in Panels A-F indicate zoomed area as shown in Panel insets. (G) A field of cultured embryonic rat hippocampal neurons viewed by differential interference contrast (DIC). (H-I) Staining with fluorophore-labeled secondary antibodies alone. Scale bars are as indicated.