Figure 1. RLIP76-expression in MEF.
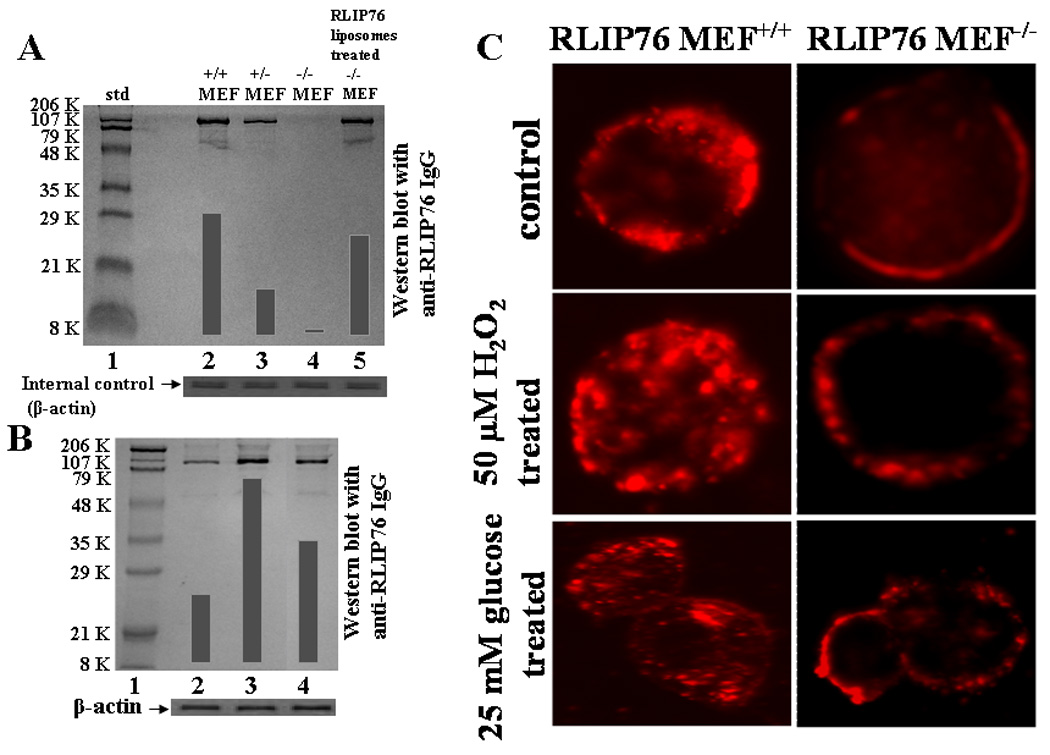
Aliquots of crude membrane fraction from RLIP76+/+, RLIP76+/−, RLIP76−/− and RLIP76−/− MEFs treated with RLIP76-liposomes (lanes 2–5, respectively), containing 200 μg protein were applied in Western-blot analyses against anti-RLIP76 IgG as the primary antibody followed by peroxidase-conjugated goat-anti-rabbit-IgG as a secondary antibody (panel A). In panel B, Western-blot for RLIP76 were performed on RLIP76+/+ MEFs (lane 2), treated with 50 μM H2O2 (lane 3) and 25 mM glucose (lane 4). Aliquots of 100 μg crude membrane fraction were loaded in SDS-PAGE, transblotted, and probed using anti-RLIP76 IgG as a primary and peroxidase-conjugated goat-anti-rabbit IgG as a secondary antibody (panel B). The blots were developed with 4-chloro-1-napthol as chromogenic substrate and developed bands were quantified by scanning densitometry. β-actin expression was used as loading control. Insulin-rhodamine Quantum dots (QD) using Confocal laser microscopy RLIP76+/+ and RLIP76−/− MEFs (0.1 × 106 cells/ml) were grown on cover slips, followed by incubation with either 50 μM H2O2 or 25 mM glucose for 20 min at 37 °C, and allowed to recover for 2 h. Cells were treated with 10% goat serum for 30 min. and labeled with molar ratio 6:1 of insulin:QD on ice for 45 min, washed and incubated for 10 min at 37 °C and fixed in cold 4% paraformaldehyde. Slides were analyzed using confocal laser-scanning microscopy (panel C).
