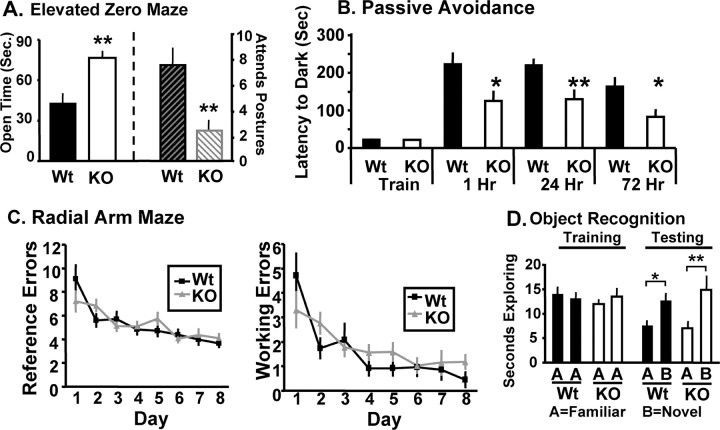
Figure 3.
Behavioral deficits in Kal7KO mice. A, In the elevated zero maze, Kal7KO mice spent more time in the open arm (p = 0.003, ANOVA) and displayed fewer stretch attend postures (p = 0.011, ANOVA) (N = 14 Wt; 9 KO) than Wt mice. B, In a passive avoidance task, Kal7KO and Wt mice exhibited no differences in training times (p = 0.895, ANOVA); compared with Wt mice, Kal7KO mice showed decreased latency to enter the dark, shock-paired side at 1 h (p = 0.03, ANOVA), 24 h (p = 0.006, ANOVA), and 72 h (p = 0.02, ANOVA) after the training session. C, In a radial arm maze acquisition task, both Wt (N = 9) and Kal7KO (N = 13) animals made an equal number of reference and working errors initially and throughout the learning sessions: left, reference errors, F(1,20) = 0.02; p = 0.888, repeated-measures two-way ANOVA; right, working errors, F(1,20) = 0.54; p = 0.469, repeated-measures two-way ANOVA. D, Both Wt (N = 11) and Kal7KO (N = 7) mice spent an equal amount of time exploring a novel object in an object recognition task (p = 0.364, Fisher's least significant difference); *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. Error bars indicate SEM.