Abstract
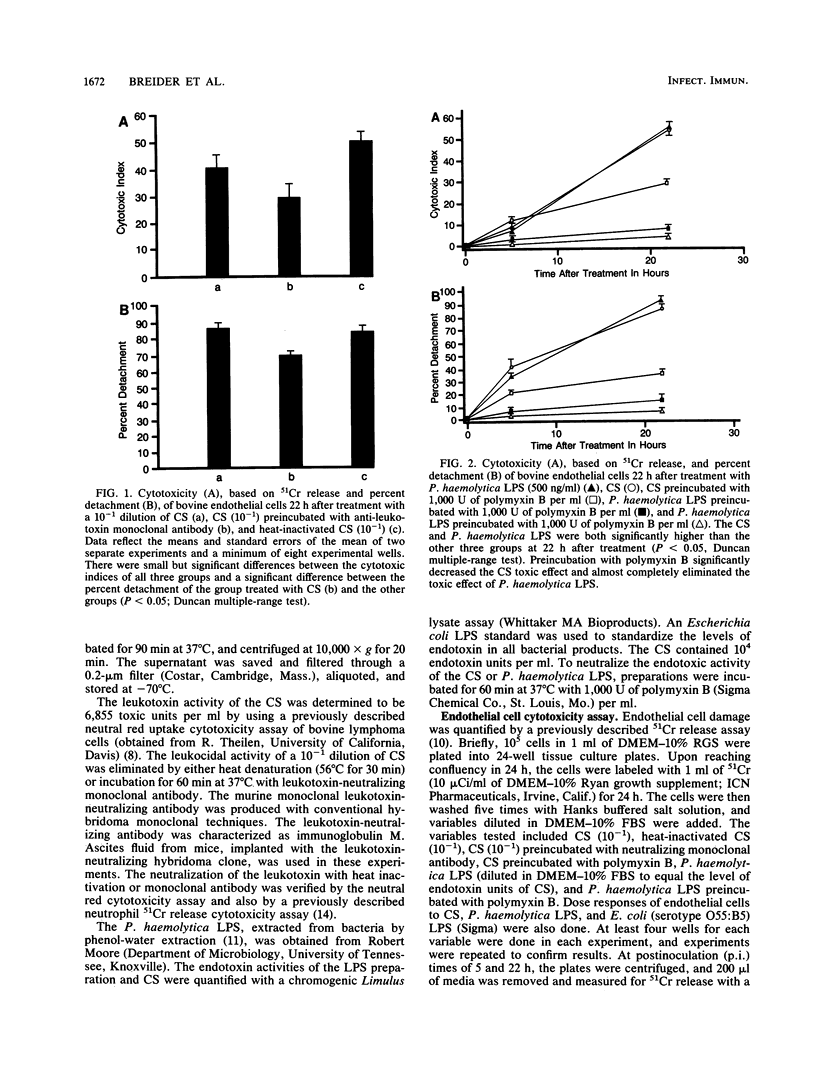
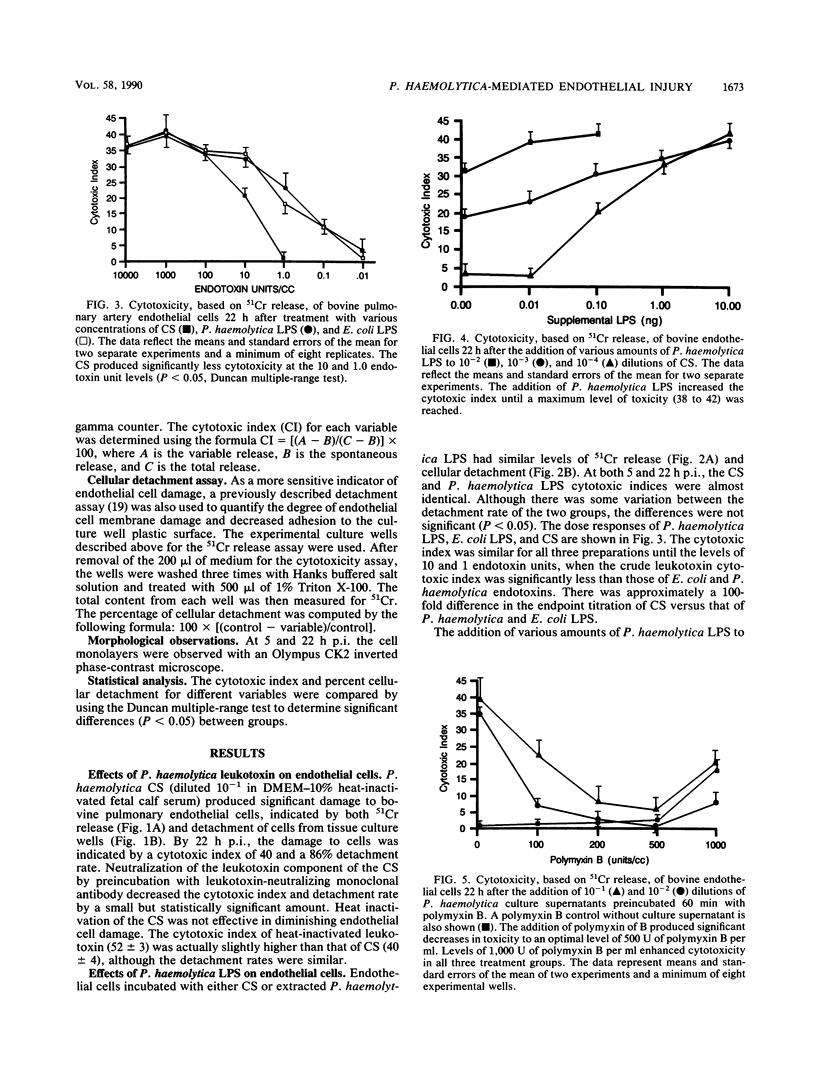
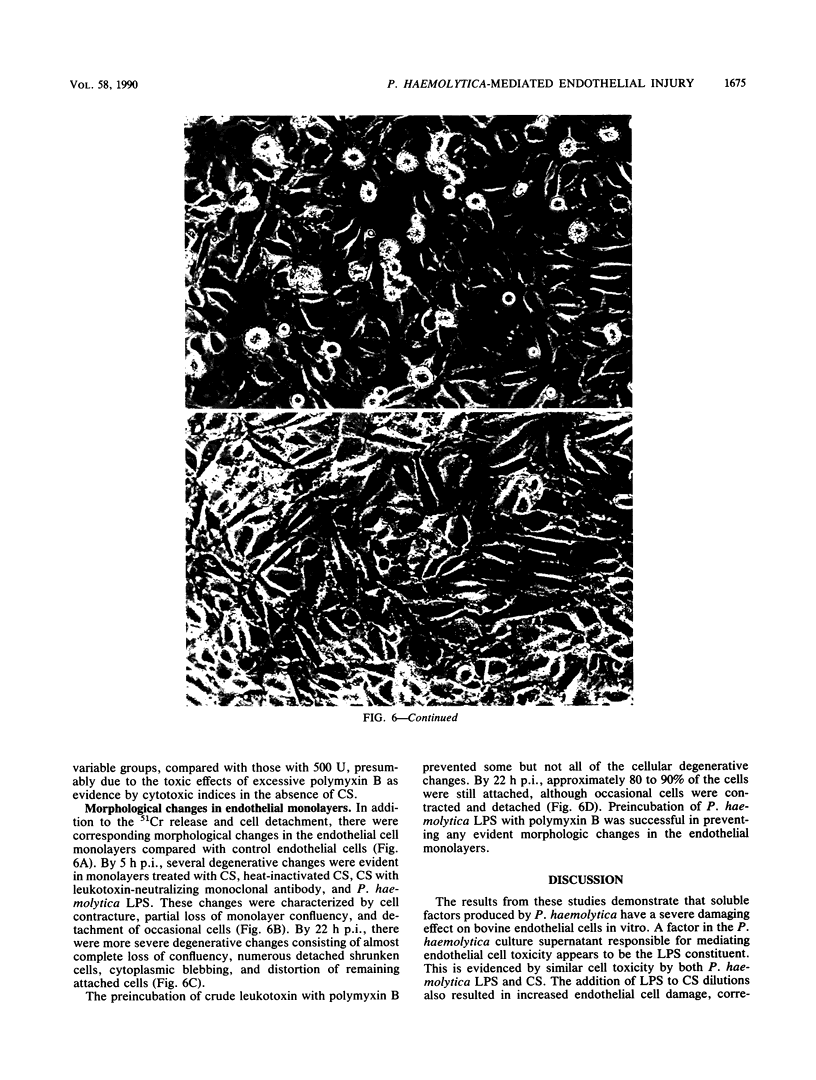
The in vitro effects of Pasteurella haemolytica components on bovine pulmonary endothelial monolayers were investigated to determine the relative role of individual bacterial factors in the pathogenesis of bovine pulmonary pasteurellosis. Bovine pulmonary endothelial monolayers were treated with P. haemolytica bacterial culture supernatant (CS) and P. haemolytica lipopolysaccharide. At 22 h postinoculation, the CS produced severe damage to the endothelial cells, indicated by high 51Cr release, extensive cellular detachment, and morphologic changes characterized by cell contraction, cytoplasmic blebbing, and loss of monolayer confluency. The neutralization of leukotoxin activity of the CS by heat inactivation was ineffective in decreasing the damage to endothelial cells; however, leukotoxin-neutralizing monoclonal antibody slightly diminished the toxic effect. P. haemolytica lipopolysaccharide by itself or as a supplement to CS produced endothelial cell damage similar to that of CS. The preincubation of CS dilutions (10(-1) and 10(-2)) or P. haemolytica lipopolysaccharide with polymyxin B almost completely eliminated cell toxicity. These studies show that P. haemolytica produces a soluble factor that is consistent with bacterial lipopolysaccharide and that is directly toxic to bovine pulmonary endothelial cells in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berggren K. A., Baluyut C. S., Simonson R. R., Bemrick W. J., Maheswaran S. K. Cytotoxic effects of Pasteurella haemolytica on bovine neutrophils. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Aug;42(8):1383–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breider M. A., Walker R. D., Hopkins F. M., Schultz T. W., Bowersock T. L. Pulmonary lesions induced by Pasteurella haemolytica in neutrophil sufficient and neutrophil deficient calves. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;52(2):205–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham K. L., Meyrick B., Berry L. C., Jr, Repine J. E. Antioxidants protect cultured bovine lung endothelial cells from injury by endotoxin. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):840–850. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Simons K. R. Effects of Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide on selected functions of bovine leukocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):154–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Chan M. K., Movat H. Z. Acute inflammation and microthrombosis induced by endotoxin, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor and their implication in gram-negative infection. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H. Serotypes of Pasteurella haemolytica in sheep in the midwestern United States. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Nov;43(11):2035–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S. L., Sieckmann D. G., Kang Y. H., Watson L. P., Homer L. D. Effects of lipopolysaccharide, lipid A, lipid X, and phorbol ester on cultured bovine endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1988 Aug;59(2):181–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer C. N., Shewen P. E. Automated colorimetric assay for the detection of Pasteurella haemolytica leucotoxin. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Jun;12(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Reidy M. A., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., Striker G. E. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated bovine endothelial cell injury in vitro. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., 2nd Neutrophils kill pulmonary endothelial cells by a hydrogen-peroxide-dependent pathway. An in vitro model of neutrophil-mediated lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Aug;130(2):209–213. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Sievert H. W., Barlow G. H., Finley R. A., Lee A. Y. Chemical, physical, biological properties of a lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K-235. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2363–2372. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B. O. Endotoxin-mediated pulmonary endothelial cell injury. Fed Proc. 1986 Jan;45(1):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Brigham K. L. Acute effects of Escherichia coli endotoxin on the pulmonary microcirculation of anesthetized sheep structure:function relationships. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):458–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. A., Lessley B. A., Confer A. W., Antone S. M., Gentry M. J. Chromatographic separation and characterization of Pasteurella haemolytica cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Oct;47(10):2233–2241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slocombe R. F., Malark J., Ingersoll R., Derksen F. J., Robinson N. E. Importance of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of acute pneumonic pasteurellosis in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Nov;46(11):2253–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbroucke-Grauls C. M., Thijssen H. M., Verhoef J. Opsonization of Staphylococcus aureus protects endothelial cells from damage by phagocytosing polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1455–1460. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1455-1460.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]