Figure 5.
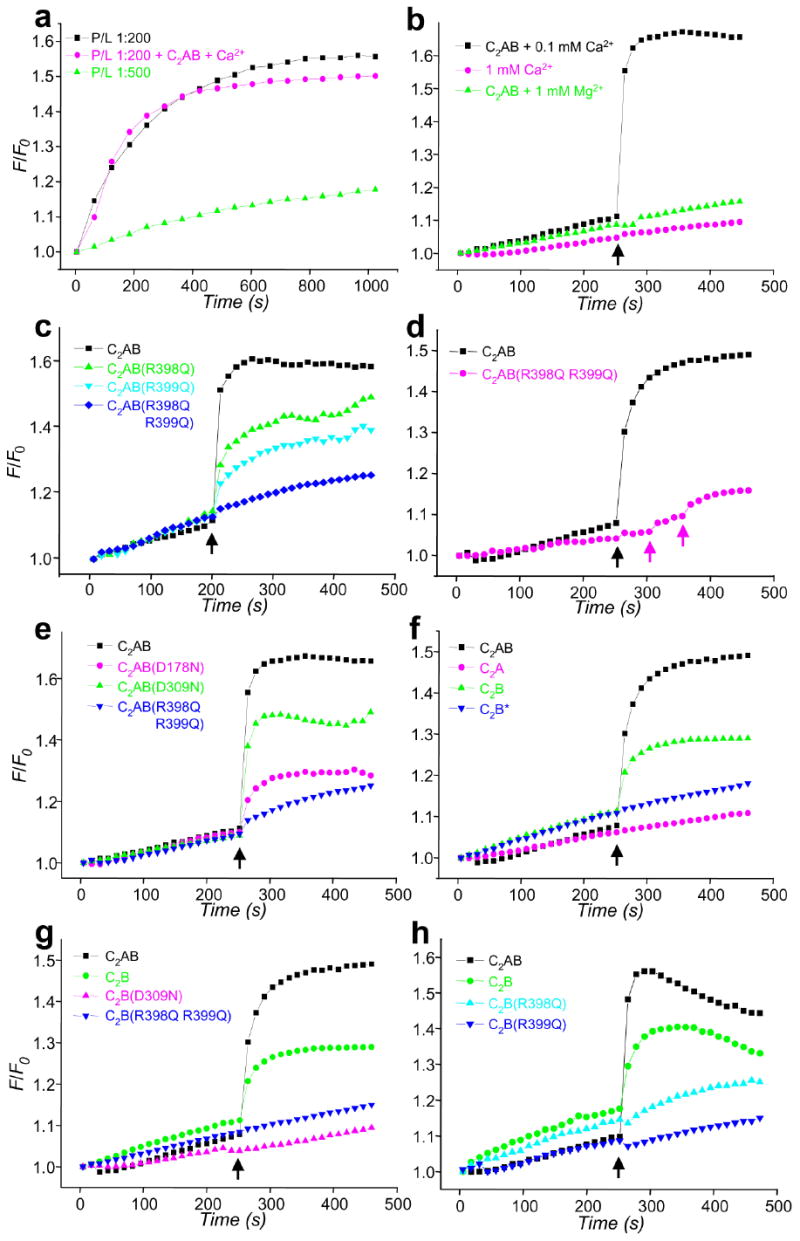
Ca2+ and synaptotagmin-1 induce a drastic increase in the rate of SNARE-mediated lipid mixing that is abolished by the R398Q,R399Q mutation. (a) Lipid mixing between synaptobrevin- and syntaxin-1/SNAP-25-containing proteoliposomes with 1:200 (black) or 1:500 (green) P/L ratios. Equal amounts of the proteoliposomes were mixed, and lipid mixing was detected by monitoring lipid fluorescence dequenching. In all experiments, the syntaxin-1/SNAP-25 liposomes were preincubated with a C-terminal synaptobrevin fragment (residues 49-96). F/F0 represents the fluorescence relative to the starting point. The pink trace shows an experiment performed with a 1:200 P/L ratio in the presence of 1 μM C2AB fragment and 100 μM Ca2+. (b-h) Lipid-mixing assays were performed as in (a) with a 1:500 P/L ratio plus different additions as indicated. Synaptotagmin-1 fragments (1 μM) were added at the beginning of the fusion reaction. In (b), Ca2+ or Mg2+ was added after 250 s of reaction (black arrows) as indicated. In (c-h), 100 μM Ca2+ was added at 250 s (black arrows). In (d), subsequent additions of 200 μM and 1 mM Ca2+ for a reaction with the C2AB-R398Q,R399Q mutant are indicated by pink arrows. WT and mutant C2B domains were purified using our standard protocol36, except for one experiment where the WT C2B domain was purified under less stringent conditions [indicated as C2B*; blue triangles in (f)]. Each set of experiments shown in each panel was performed on the same day with the same proteoliposome preparations.
